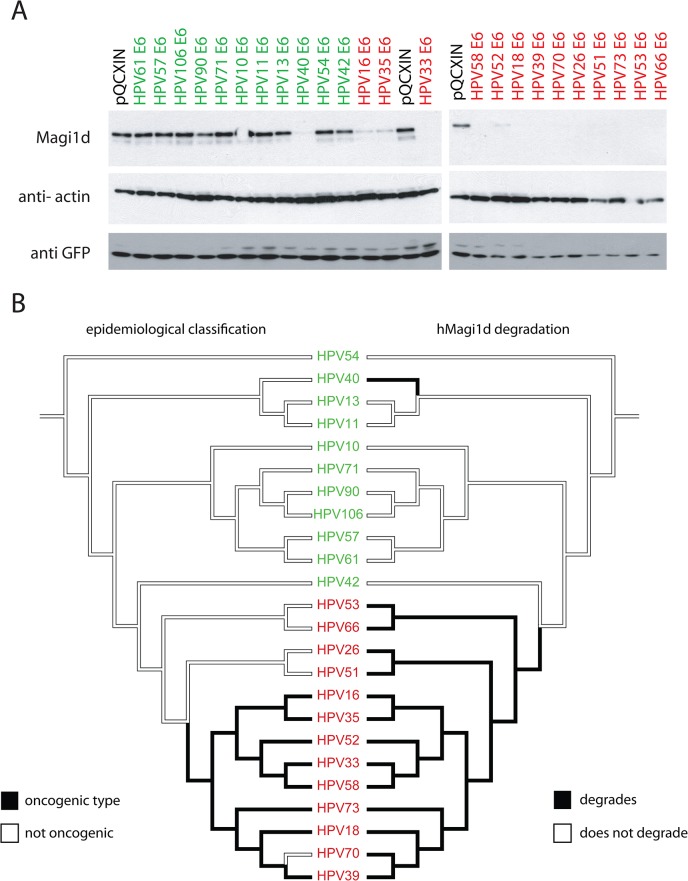
Fig 2. All members of the phylogenetic high-risk clade degrade human MAGI1d.
(A) C-33A cells were transfected with 24 different E6 proteins covering the known evolutionary spectrum within the Alphapapillomavirus genus. The western blot shows a representative experiment. GFP was probed as a transfection control indicating equal transfection. This figure shows that all High-Risk types (highlighted in red) target hMAGI1d for degradation. The pQCXIN vector was used as control. (B) Mirror trees comparing the epidemiological (left) and PDZ-protein degradation (right) phenotypes on the E6 based phylogeny. The viral names are colored according to phylogenetic classification. High-risk viruses are colored in red, while LR viruses are colored green. The branches of the tree are shaded according to the state of each character under investigation.