Fig 3. The effect of LVFX on lung damage and viral titer in influenza virus-infected mice.
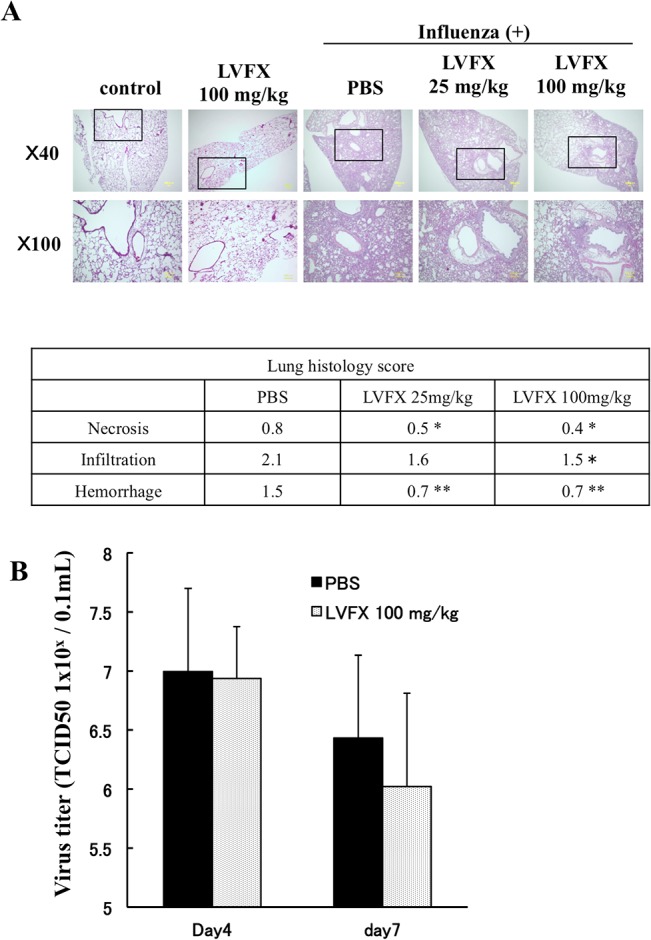
(A) Section of lung tissue were prepared at the day 7 after influenza virus infection, and subjected to histopathological examination with HE staining (upper). The alveolar space was observed in lungs from control mice, however the influenza virus infection caused a marked increase in the infiltration of inflammatory cells into the alveoli or peribronchial areas, and the alveolar space was completely filled with these cells. Treatment with LVFX at a dose of 100 mg/kg decreased the overall infiltration of inflammatory cells. The histopathological severity of lung section was determined and average score showed in lower of HE staining image. Histological score shown PBS (n = 4), 25 mg/kg LVFX (n = 5) and 100 mg/kg LVFX (n = 5). (B) The effect of LVFX on viral load at day 4 and 7 were determined using a plaque forming assay. Each bar represents the mean ± SD (n = 3–5). *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs PBS.
