Fig 6. Suggested mechanisms of doxorubicin induced nephropathy.
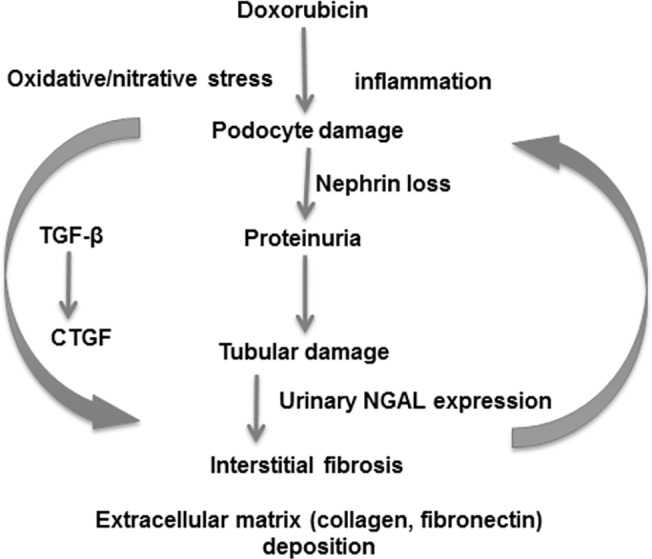
A single administration of doxorubicin induced podocyte damage demonstrated by loss of nephrin and leading to proteinuria. Proteinuria damages tubules as demonstrated by increased urinary NGAL excretion. Tubular damage leads to interstitial inflammation and fibrosis with collagen and fibronectin deposition. Inflammation is accompanied by oxidative/nitrative damage triggering further immune activation. Reverse arrows symbolize main elements of the vicious circle. Sustained injury activates the TGF-β1 and CTGF profibrotic axis. Sustained injury eventually leads to fibrotic end-stage kidney. NGAL: neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin; TGF-β1: transforming growth factor β1; CTGF: connective tissue growth factor.
