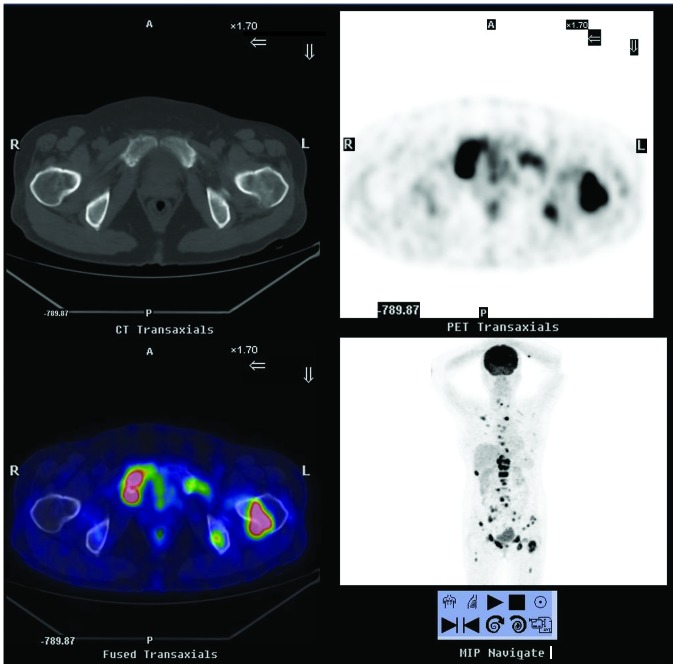
Figure 1.
18F-FDG PET/CT scintigraphy from September 2011, showing extensive bone destruction with hypermetabolic osteolysis in the skull, spine, sternum, certain ribs, bilateral scapulas, ilia, pubis, ischia and left femur, which had increased 18F-FDG uptake. 18F-FDG PET/CT, 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography; A, anterior; P, posterior; R, right; L, left.