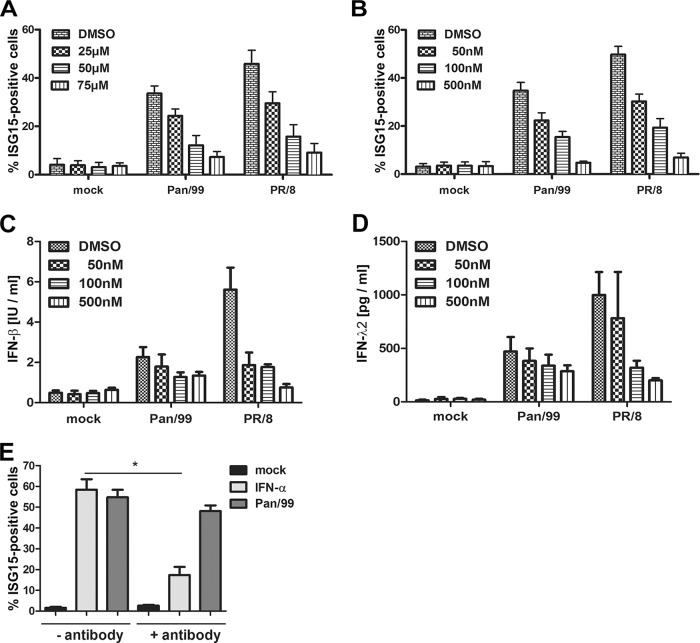
FIG 2.
ISG15 induction during IAV infection depends on NF-κB and JAK1/TYK2 signaling. A549 cells were pretreated with BAY 11-7085 to inhibit NF-κB (A) or with JAK inhibitor I to inhibit JAK1/TYK2 (B to D) for 1 h prior to mock treatment or infection with Pan/99 or PR/8 IAV at an MOI of 0.5 for 16 h. The inhibitors were present throughout the experiments, and their concentrations are indicated. Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was used as a control. (A and B) Bars represent percentages of total ISG15-positive cells as assessed by FACS. Data are means + SEM for experiments conducted in duplicate (n = 3). IFN-β (C) and IFN-λ2 (D) levels in supernatants taken 16 h after infection with the different viruses were assessed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Data are means + SEM for experiments conducted in duplicate (n = 3). (E) To examine the role of type I IFN signaling, A549 cells were not treated or pretreated with 15 μg/ml anti-IFNAR2 neutralizing antibody for 8 h. Subsequently, the cells were mock treated, stimulated with 50 U/ml IFN-α, or infected with Pan/99 at an MOI of 1 for 16 h. The antibody was present or absent throughout the experiments, as indicated. Bars represent percentages of total ISG15-positive cells as assessed by FACS. Data are means + SEM (n = 4). *, P < 0.05 (Mann-Whitney U test).