FIG 3.
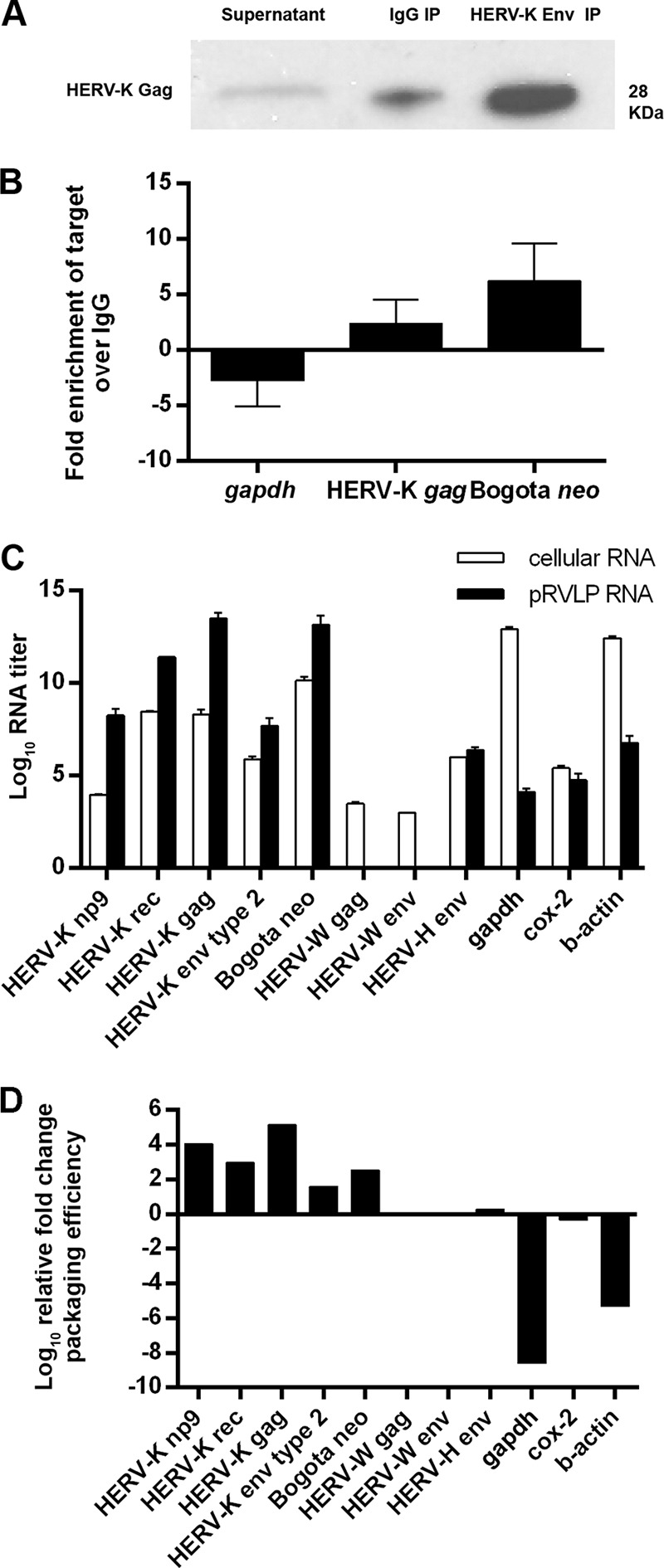
Packaging of Bogota transcripts in HK2 viral particles. (A and B) Immunoprecipitation of HERV-K virions containing Bogota transcripts. NCCIT cells were transfected with HERV-KBogota neo, and viral particles were collected 48 h after. Viral particles were pelleted by ultracentrifugation prior to immunoprecipitation with either an anti-HERV-K Env antibody or a control anti-mouse IgG2a. (A) Cleared supernatant and the immunoprecipitated samples were analyzed for HERV-K capsid enrichment by Western blotting with an anti-HERV-K Gag antibody. The untreated supernatant is about 5-fold diluted compared to the volumes obtained in the concentrated and immunoprecipitated samples; therefore, equal amounts of the supernatants could not be added in the gel due to well-volume constraints. The low background level detected with the anti-IgG2a immunoprecipitation may be nonspecific. (B) RNA from immunoprecipitated particles was quantitated for HERV-K gag, Bogota neo, or nonviral gapdh by qRT-PCR. The average fold enrichment for each target in particles precipitated with anti-HERV-K Env compared to those precipitated by control anti-mouse IgG2a is shown. (C) RNA expression levels of HERV-K (np9, rec, gag, and env type 2), Bogota neo, HERV-W (gag and env), HERV-H env, gapdh, cox-2, and β-actin were analyzed by qRT-PCR in Bogota-transfected NCCIT cells (white bars) and pelleted retrovirus-like particles (pRVLPs; black bars). The log10 RNA titers show the average quantitations ± standard deviations (SD) from at least three independent experiments expressed in arbitrary units. (D) Packaging efficiency of Bogota transcripts in NCCIT-produced viral particles. The relative fold change of packaging efficiency was calculated by dividing expression levels of target RNA copies in NCCIT pRVLPs by their expression levels in total cellular RNA. Values are presented as the means ± SD from at least three independent experiments. A value of 0 is given for HERV-W gag and env due to the absence of these transcripts from NCCIT pRVLPs.
