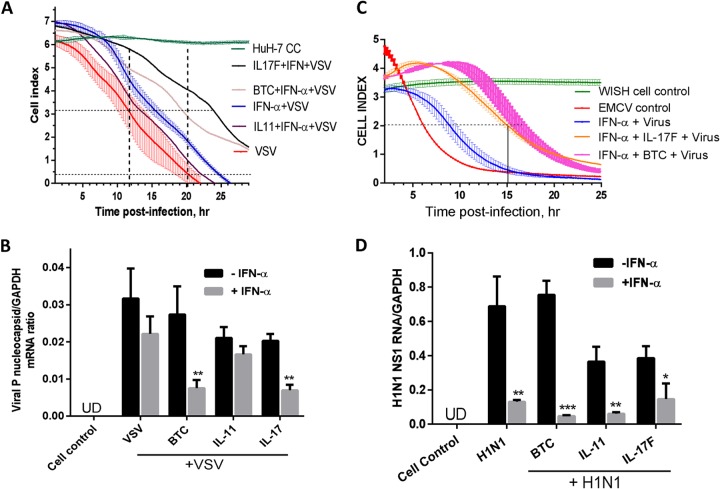
FIG 7.
Antiviral activities of cytokines and IFN combinations. (A) Huh-7 cells were seeded for overnight incubation in microwell plates precoated with micro-electronic chip electrodes. The cells were treated with the indicated cytokines and combinations with IFN-α and challenged with VSV at an MOI of 1. The CPE was monitored at 15-min intervals in real time. The cell index, representing live-cell activity in relation to time postinfection is presented as means ± SEM from triplicate wells. (B) Huh-7 cells were treated with the indicated cytokines in the presence or absence of IFN-α (10 IU/ml) for 16 h and then infected with VSV at an MOI of 1 for 6 h. Total RNA was extracted, and VSV nucleocapsid P RNA levels were assayed by RT-qPCR with primers specific for VSV P RNA. GAPDH mRNA was used as a control. UD, undetectable. (C) WISH cells were seeded in microwell plates precoated with micro-electronic chip electrodes. The cells were treated with the indicated cytokines and/or combinations with IFN-α and challenged with EMCV at an MOI of 0.1. The CPE was monitored at 15-min intervals in real time. The cell index, representing live-cell activity in relation to time postinfection, is presented as means ± SEM from triplicate wells. The results are from one representative experiment out of two. The horizontal line shows ED50 readings. (D) Confluent A549 lung cells were treated with cytokines (3 nM) in the presence or absence of IFN-α (100 IU/ml) for 16 h. The cells were infected with the human influenza virus H1N1 for 6 h, and then the RNA was extracted and assayed for H1N1 NS1 RNA using RT-qPCR with primers specific for H1N1 NS1. GAPDH was also measured as a control. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.