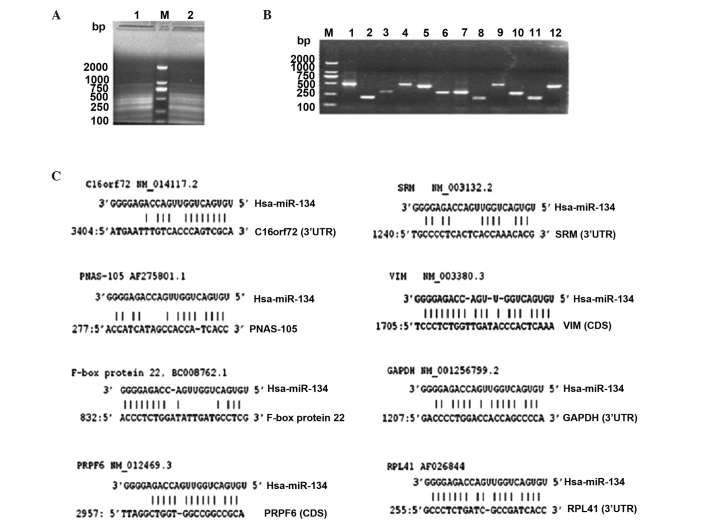
Figure 2.
Hybrid-PCR was applied and 8 putative target mRNAs of miR-134 were identified in SKOV3-TR30 cells. (A) Hybrid-PCR was conducted as described. Products of hybrid-PCR were subjected to electrophoresis on 2% agarose gel with DL2000 alongside. Lines 1 and 2 show that the amplification products from hybrid-PCR were variable in length. M: DL2,000 marker. (B) All Hybrid-PCR products were purified and cloned into T-vector. After picking the positive colony forming units, M13 primers were used to identify the insertions in order to further sequence. Lines 1–12 are the elementary identification results of positive colony forming units which contain hybrid-PCR products. Lines 2.8.11 are the negative which represent the empty T vectors, while the remainder represent the positive clones, indicating target mRNAs of hybrid-PCR products were successfully inserted into the T-vector. M: marker DL2000. (C) Overall eight putative target mRNAs of hsa-miR-134 in SKOV3-TR30 cells were obtained. Putative binding sites of each gene were shown. Among them, target sites of vimentin and PRPF6 were not located in 3′ untranslated region but rather in the coding region. PCR, polymerase chain reaction.