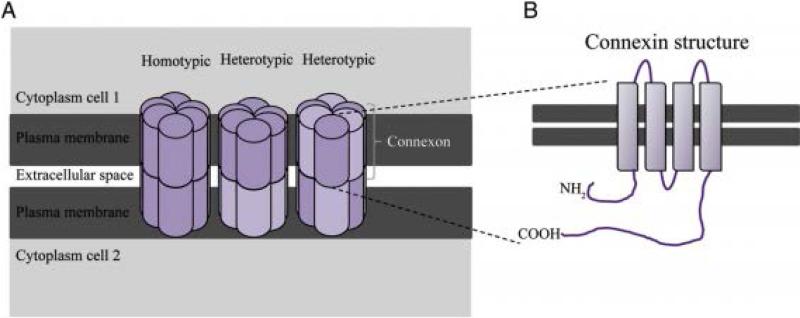
Figure 2.
A. Schematic representation of hemichannels or connexons from neighboring cells docking to form functional gap junctions that enable communication between the cytoplasm of cell 1 and the cytoplasm of cell 2. Connexons can be assembled from the same subset of connexins (homomeric) or different subsets of connexins (heteromeric). Moreover, gap junctions can present either identical connexon composition of connexin subtypes (homotypic) or different connexon composition of connexin subtypes (heterotypic). B. Connexins are transmembrane proteins composed of four transmembrane domains with alpha helix, two extracellular loops and an intracellular loop. Both N- and C-terminals are intracellular. The two extracellular loops contain three highly conserved cysteine residues responsible for the selectivity of hemichannel interactions.