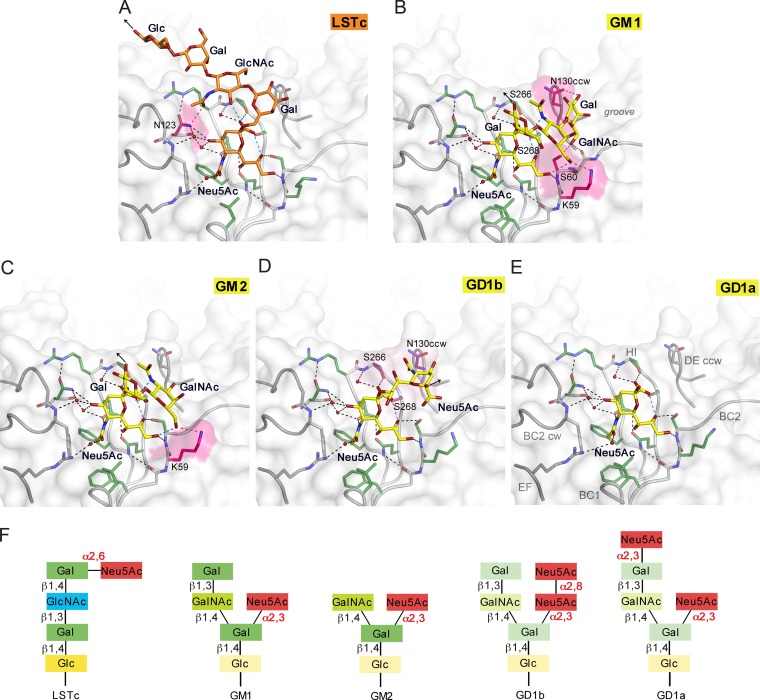
FIG 2.
JCPyV WT3 interacts with α2,3-, α2,6-linked Neu5Ac and α2,8-, α2,3-di-Neu5Ac in a highly plastic binding site. (A to E) Structures of WT3 VP1 bound to LSTc (A), GM1 (B), GM2 (C), GD1b (D), and GD1a (E) glycans. VP1 is shown in surface and cartoon representation. Residues involved in polar or van der Waals interactions in only one of the glycan complex structures are highlighted in pink or purple, respectively. Interactions are depicted using dashed lines, with direct and water-mediated contacts with the glycans in black, intramolecular interactions of glycans in blue, and interaction with either LSTc, GM1, or GM2 in pink. Glycans are shown in stick representation and colored according to atom type, with nitrogens in blue, oxygens in red, and carbons in orange for LSTc and in yellow for ganglioside-derived glycans, respectively. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. Black arrows indicate the part of LSTc that is linked to a lipid or protein (A), the direction of Glc that is further linked to the lipid in the context of the GM1 and GM2 gangliosides (B and C), and the O2 of the second Neu5Ac, to which the Gal residue within the branched GD1b ganglioside motif is attached (D). (F) Glycans used for comparative binding studies. Additionally, the GT1b ganglioside was used in cell supplementation assays. GT1b features, compared to GD1b, an additional α2,3-linked Neu5Ac at the Gal in the left arm of the branched motif.