FIG 3.
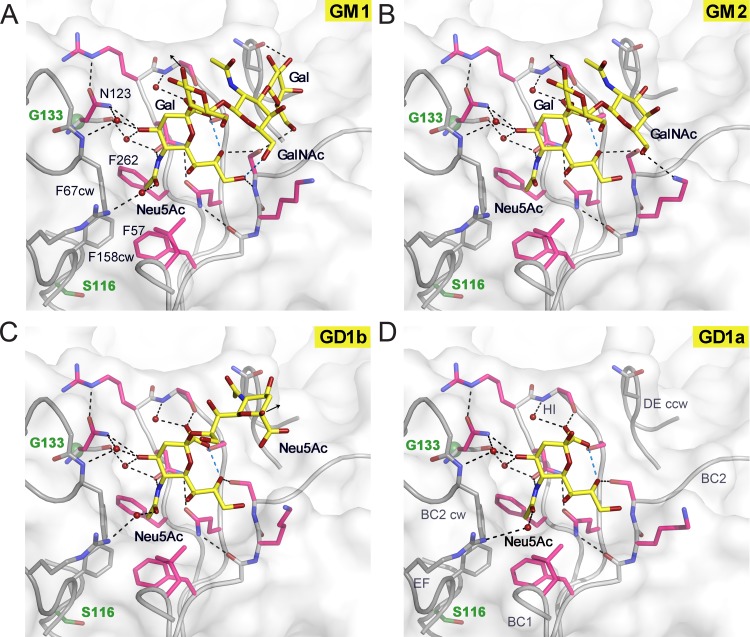
JCPyV Mad-1 engages α2,3-, α2,6-linked Neu5Ac and α2,8-, α2,3-di-Neu5Ac highly similarly to WT3. Complex structures of Mad-1 VP1 with GM1 (A), GM2 (B), GD1b (C), and GD1a (D) ganglioside glycans are shown. VP1 is shown in surface and cartoon representation. Interactions are depicted by dashed lines, with direct and water-mediated contacts with the glycans in black and intramolecular interactions of glycans in blue. VP1 amino acid differences between Mad-1 and WT3 are located predominantly within or close to the surface loops. Residue glycine 133 (green), which is an alanine in WT3, is located beneath N123, which undergoes an induced-fit movement to accommodate the terminal Neu5Ac during glycan engagement (21). Mad-1 residue serine 116, a threonine in WT3, is located below the hydrophobic cavity of the binding site that is formed by F67CW, F158CW, F57, and F262 and encloses the Neu5Ac N-acetyl group. The three additional mutations in WT3 VP1, R74K, L157V, and K163T, are distant from the binding site and are not shown in the close-up views.