FIG 3.
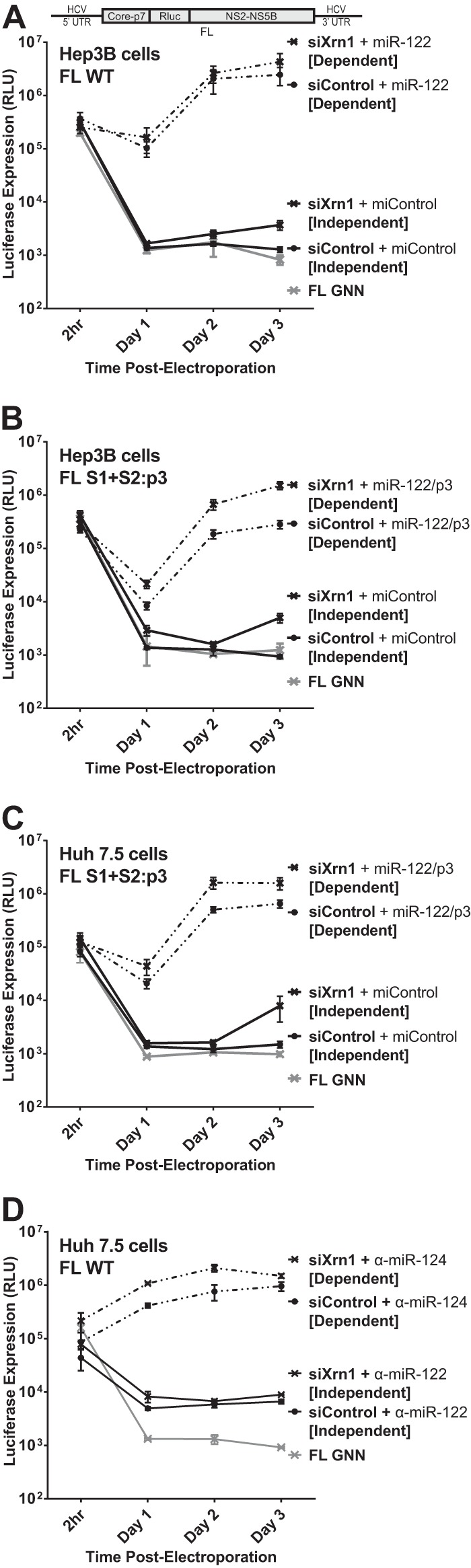
Knockdown of Xrn1 enhances full-length J6/JFH-1 viral RNA (FL WT) replication and permits detectable replication of full-length RNA in the absence of miR-122 binding. (A) Hep3B cells were electroporated with siXrn1 or siControl as described for Fig. 1B to knock down Xrn1. The effects of Xrn1 knockdown were assessed on replication of wild-type full-length J6/JFH-1 viral RNA “FL WT,” encoding an in-frame Renilla luciferase reporter (depiction above), miR-122-dependent replication was assessed in cells coelectroporated with miR-122, while miR-122-independent replication was assessed in cells coelectroporated with miControl. FL GNN is a full-length genome with a GDD-to-GNN polymerase-inactivating mutation to determine background Renilla luciferase expression in the absence of HCV RNA replication. (B) Hep3B cells were electroporated with siXrn1 or siControl to assess the influence of Xrn1 knockdown on HCV replication as described for Fig. 1B, but in this case miR-122-independent replication was evaluated using the miR-122 binding site mutant full-length J6/JFH-1 viral RNA FL S1+S2:p3, a full-length mutant with the p3 mutation in miR-122 binding sites S1 and S2 that does not respond to wild-type miR-122. miR-122-dependent replication was assessed in cells coelectroporated with miR-122/p3, an miR-122 mimic bearing a G-to-C mutation at position 3 that restores binding to the mutant genome. (C) Huh7.5 cells were electroporated with siXrn1 or siControl as described for Fig. 1F, and the effect of Xrn1 knockdown on miR-122-independent replication or miR-122-dependent replication of full-length J6/JFH-1 viral RNA was assessed in cells coelectroporated with FL S1+S2:p3 and miControl or miR-122/p3, respectively. (D) Huh7.5 cells were treated as described for panel C but were electroporated with wild-type full-length J6/JFH-1 viral RNA (FL WT). To establish miR-122-independent replication, the cells were treated with an miR-122 antagonist (α-miR-122) or a control miRNA antagonist targeting miR-124 (α-miR-124).
