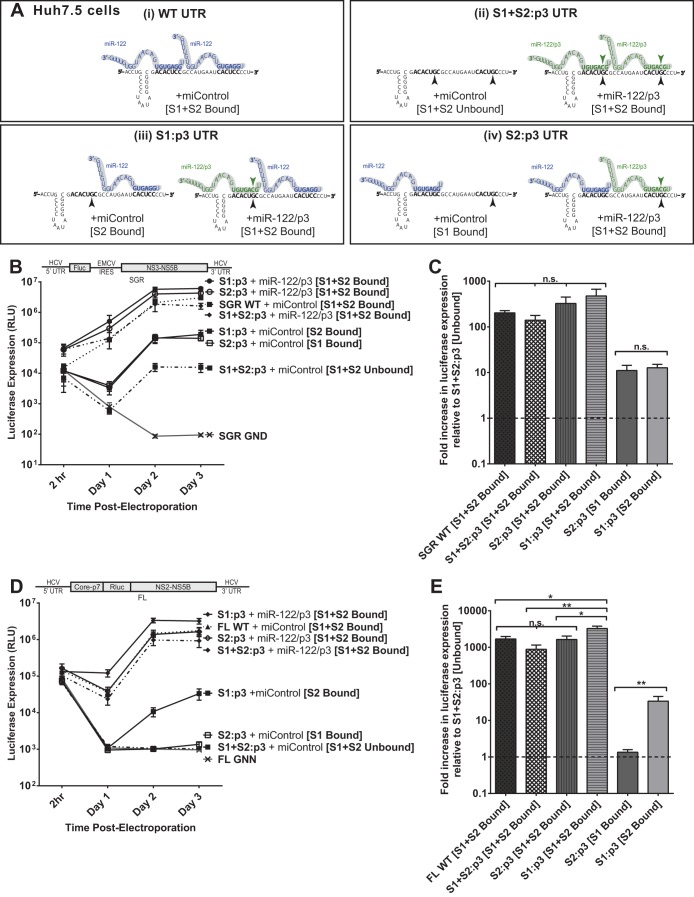
FIG 4.
The impact of miR-122 binding at site 1 compared to binding at site 2 with subgenomic and full-length replicons in Huh7.5 cells. (A) By mutating either S1 or S2 to the p3 mutation and supplementing with miR-122/p3 as shown, we can specifically analyze the influence of miR-122 binding to both sites (i), neither site (ii), or each site alone, as in panels iii and iv. (B) To assess the influence of miR-122 binding to each site, Huh7.5 cells were electroporated with subgenomic HCV RNA bearing the p3 C-to-G mutation in miR-122 binding site S1 (S1:p3) or in binding site S2 (S2:p3). To assess replication of all constructs when both sites are occupied, the S1 and S2:p3 RNAs were supplemented with miR-122/p3 as shown in panel A, wild-type HCV RNA replication was supplemented with miControl, and the S1+S2:p3 double-binding site mutant was supplemented with miR-122/p3 as shown in panel Ai. Replication in the absence of miR-122 binding was assessed using S1+S2:p3 HCV RNA replication with miControl, where neither binding site was occupied. For the determination of background luciferase expression in the absence of replication, SGR GND RNA bearing a GDD-to-GND polymerase-inactivating mutation was used. Replication was measured by firefly luciferase expression at the indicated time points. (C) The fold increase in HCV replication induced by miR-122 binding at 3 days postelectroporation over that observed using miR-122-unbound subgenomic viral RNA, S1+S2:p3 [S1+S2 Unbound], dotted line. Significance for relevant comparisons was determined by unpaired parametric t test. (D) Experiments similar to those presented in panel B were done to assess the influence of miR-122 binding to each site on full-length HCV RNA. Huh7.5 cells were electroporated with full-length HCV RNA bearing the p3 mutation in miR-122 binding site S1 or S2 and were supplemented with miRNAs and evaluated as described for panel B. Replication was measured by Renilla luciferase expression at the indicated time points; the FL GNN polymerase-inactivated mutant is a no-replication control. (E) The fold increase in HCV replication induced by miR-122 binding at site S1 or S2 was evaluated as described for panel C. Significance for relevant comparisons was determined by unpaired parametric t test.