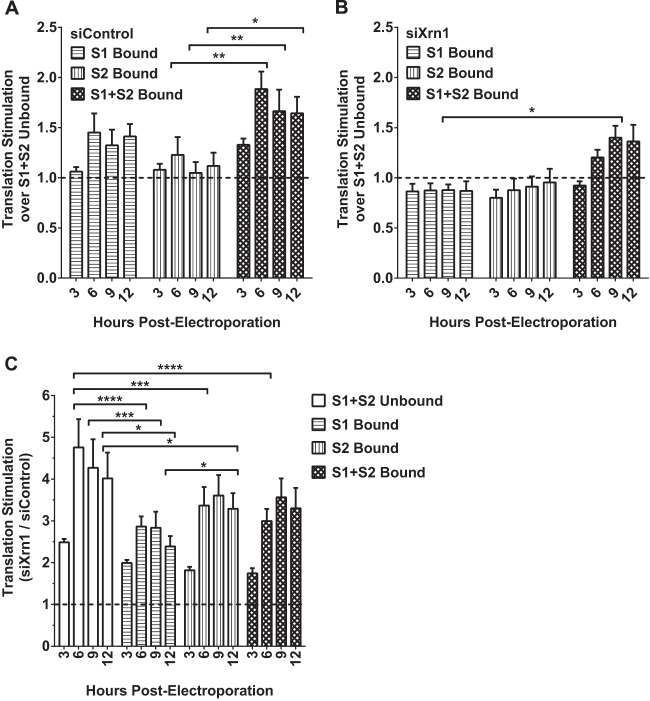
FIG 9.
Knockdown of Xrn1 increases FL S1:p3 RNA translation overall but reduces the contribution miR-122 binding makes to viral translation. Hep3B cells were electroporated with siXrn1 or siControl for preknockdown. Three days later, cells were electroporated with FL S1:p3 GNN (replication-incompetent S1 miR-122 binding mutant) viral RNA, transfection control firefly mRNA, and the indicated miRNAs as depicted in Fig. 5Aiii. Because the viral RNA is replication incompetent, measuring luciferase at the indicated 3, 6, 9, and 12 h post-second electroporation measures viral translation. Viral translation was normalized to transfection control mRNA firefly luciferase expression levels measured at 3 h post-second electroporation. The effect on translation of FL S1:p3 GNN viral RNA by miRNA binding at S1, S2, or both sites was compared to translation when neither site was bound in siControl-treated cells (A) or siXrn1-treated cells (B), where the dotted line represents 1-fold or no increase in translation. (C) Stimulation of translation by Xrn1 was determined by comparing normalized viral translation in siXrn1-treated cells to viral translation in siControl-treated cells. The dotted line indicates 1-fold or no stimulation of viral translation. Significance for all figures was determined using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), with Tukey's multiple-comparison test performed to compare differences of samples within a given time point. Only significant differences are indicated; all other comparisons were not significant.