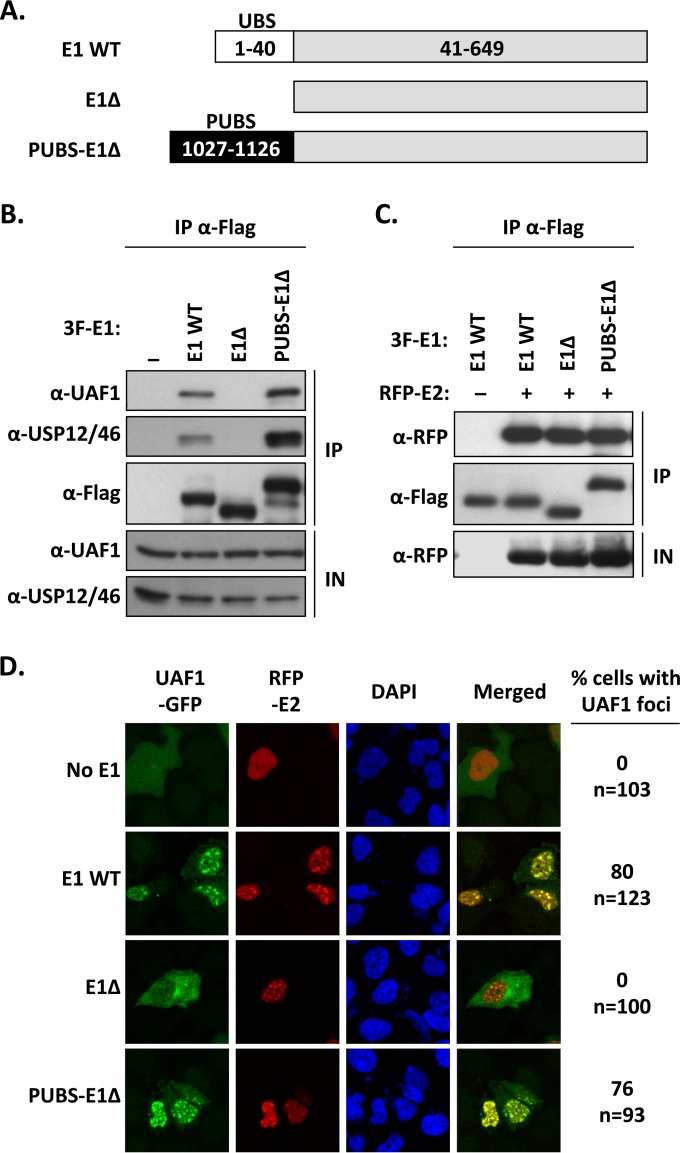
FIG 4.
The chimeric PUBS-E1Δ helicase interacts with UAF1 and HPV E2 in nuclear foci. (A) Schematic representation of the different E1 proteins. The wild-type protein (WT E1) is represented by a gray bar with its N-terminal UBS indicated by a white box. The E1Δ protein lacks the first 40 amino acids encompassing the E1 UBS. In the PUBS-E1Δ chimeric helicase, the E1 UBS has been replaced by the analogous domain from PHLPP1 (PUBS, black box). Amino acid boundaries of each protein fragment are indicated. All three E1 proteins are tagged with a 3F epitope at their N terminus (not shown). (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of endogenous UAF1 and USP46 with the PUBS-E1Δ protein. C33A cells were transfected with an expression plasmid for 3F-tagged PUBS-E1Δ protein or with 3F-WT E1 as a positive control or 3F-E1Δ protein as a negative control. E1 proteins were immunoprecipitated with an anti-Flag antibody, and the presence of UAF1 and USP12/46 in the immunoprecipitates (IP) and input cell extracts (IN) was analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies against these two proteins. (C) Coimmunoprecipitation of HPV E2. Coimmunoprecipitation experiments were performed as described above but using C33A cells cotransfected with an RFP-E2 expression vector. The ability of the indicated E1 proteins to interact with E2 was determined by probing the immunoprecipitates with an anti-RFP antibody. (D) Fluorescence confocal microscopy showing the intracellular localization of UAF1-GFP and RFP-E2 in cells expressing one of the indicated E1 proteins. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. For each condition, the percentage of cells in which UAF1-GFP is present within E2-containing nuclear foci is indicated on the left. The total number of transfected cells analyzed (n=) is specified underneath the percentage.