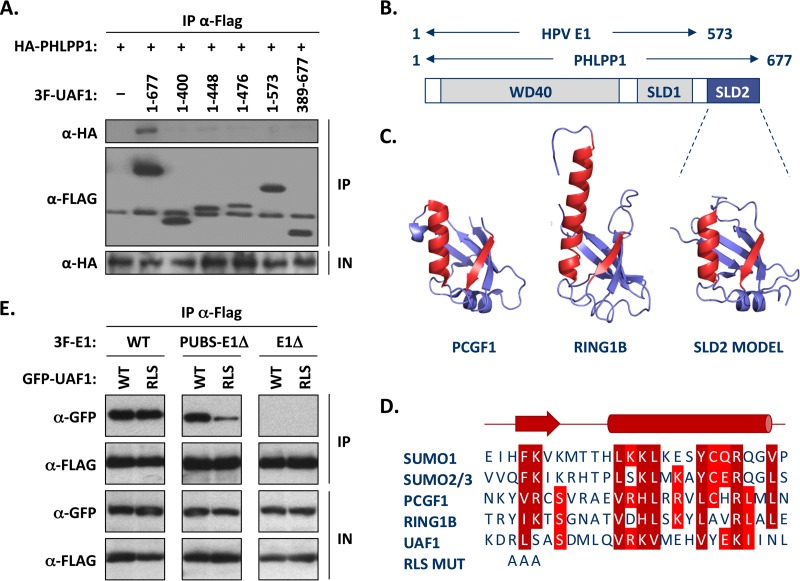
FIG 8.
The WD repeat region and C-terminal SUMO-like domain of UAF1 are required for interaction with PHLPP1 and PUBS-E1Δ proteins. (A) Mapping of the UAF1 domain required for interaction with PHLPP1, by coimmunoprecipitation. C33A cells were cotransfected with an expression vector for HA-tagged PHLPP1 together with a plasmid encoding 3F-UAF1 or the indicated truncated derivative. The amino acid boundaries of each UAF1 fragment are indicated. UAF1 proteins were immunoprecipitated with an anti-Flag antibody and the presence of HA-PHLPP1 in each immunoprecipitate (IP) and input cell extract (IN) tested by Western blotting with an anti-HA antibody. Only the full-length UAF1 protein could interact with PHLPP1 in this assay. (B) Schematic representation of UAF1 showing the location of the WD40 repeat region and of the two SUMO-like domains (SLD1 and SLD2). The regions of UAF1 needed for interaction with PHLPP1 (aa 1 to 677) and with E1 (aa 1 to 573) (8) are summarized above. (C) Homology model of SLD2 from human UAF1 based on the RAWUL domains of PCGF1 (34), RING1B (35), and related proteins. The structures of PCGF1 (PDB 4HPM) and RING1B (PDB 3GS2) are shown for comparison. The β-strand and α-helix that make up part of the interaction surface on PCGF1 and other SUMO-like domains are colored in red, and their sequences are aligned below. (D) Amino acid sequence alignment of the β-strand and α-helix of SUMO1 to SUMO3, PCGF1, and RING1B with UAF1 SLD2. RLS MUT refers to the mutation introduced in the β-strand of UAF1 that changes the RLS sequence to three alanines. (E) Coimmunoprecipitation of wild-type and RLS-mutated UAF1 with either wild-type E1 (WT), PUBS-E1Δ, or E1Δ protein. C33A cells were cotransfected with an expression vector for the indicated 3F-E1 protein together with a plasmid encoding either wild-type or RLS mutant GFP-UAF1. Following the immunoprecipitation of E1 with an anti-Flag antibody, the presence of GFP-UAF1 in each immunoprecipitate (IP) and input cell extract (IP) was tested by Western blotting with anti-GFP antibodies.