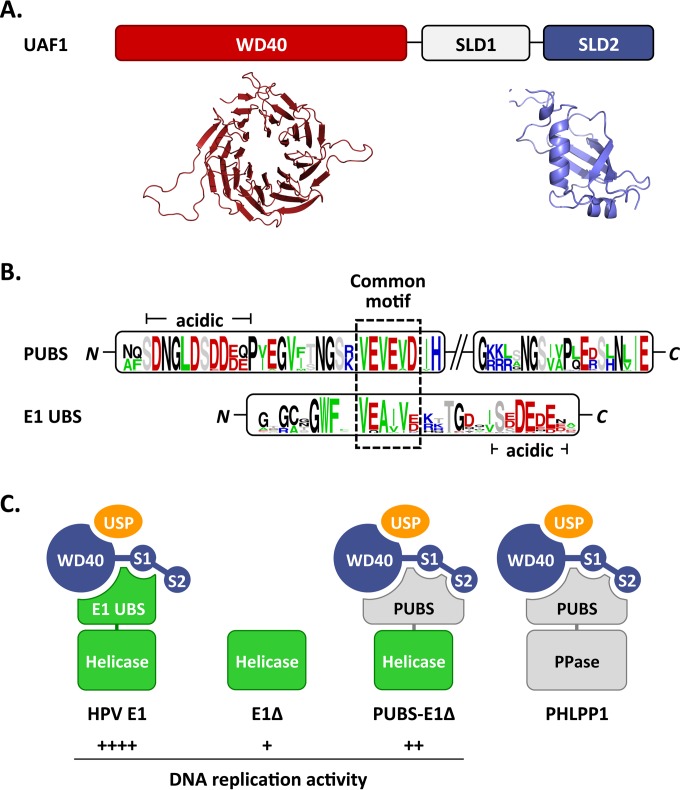
FIG 9.
Proposed interactions between HPV E1, PHLPP1, and UAF1-containing deubiquitinating enzymes. (A) Schematic representation of UAF1 showing the WD repeat region and two SUMO-like domains (SLD1 and SLD2). A structural model of the WD repeat region of human UAF1 obtained from the WDSP database (40) is presented underneath (colored in red), together with the model of SLD2 generated in this study (colored in blue). (B) Sequence logos of the PHLPP1 UBS (PUBS) and E1 UBS. Only the conserved N- and C-terminal regions of PUBS are shown. A sequence motif conserved between the N-terminal region of PUBS and the E1 UBS is boxed. A stretch of negatively charged amino acids found in both UBSs is also indicated (acidic). (C) Cartoon representation of the proposed complexes formed by E1 and PHLPP1 with UAF1-containing deubiquitinating enzymes. UAF1 is represented as a tripartite protein (blue) comprised of a WD40 repeat region and of two SUMO-like domains, SLD1 (S1) and SLD2 (S2). USP1, USP12, and USP46, which form mutually exclusive complexes with the WD repeat region of UAF1, are represented by a yellow oval. HPV E1 is diagrammed as a bipartite protein (green) comprised of a helicase domain linked to the E1 UBS, which contacts UAF1 independently of SLD2. This UBS is missing in the E1Δ protein and replaced by the PHLPP1 UBS in the PUBS-E1Δ chimeric enzyme. PHLPP1 is also shown as a bipartite protein (gray) made of a phosphatase domain (PPase) attached to PUBS, which requires all three subdomains of UAF1 for interaction. The relative levels of HPV DNA replication supported by the proposed E1-containing complexes are indicated by plus signs.