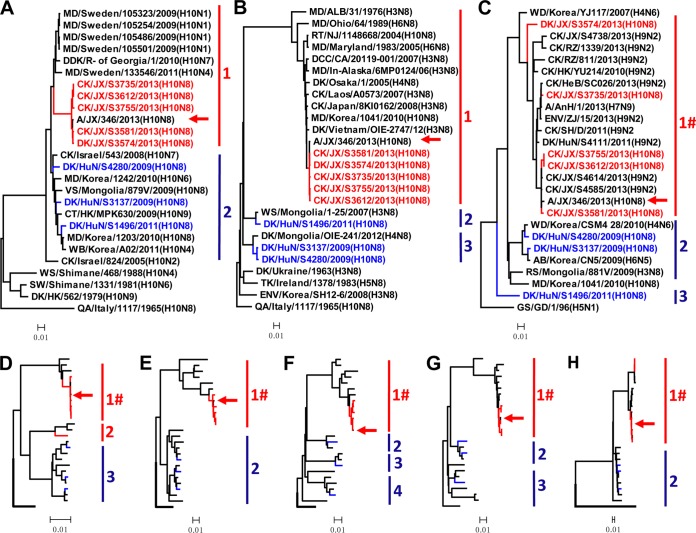
FIG 1.
Phylogenetic analyses of H10N8 viruses isolated between 2009 and 2013 in China. The phylogenetic trees were generated with the PHYLIP program of the CLUSTALX software package (version 1.81). The trees were generated based on the following sequences: HA nucleotides 22 to 1704, NA nucleotides 19 to 1416, PB2 nucleotides 28 to 2307, PB1 nucleotides 25 to 2298, PA nucleotides 25 to 2175, NP nucleotides 46 to 1542, M nucleotides 26 to 1007, and NS nucleotides 27 to 864. The phylogenetic trees of HA (A) and NA (B) were rooted to A/Quail/Italy/1965(H10N8), and those of PB2 (C), PB1 (D), PA (E), NP (F), M (G), and NS (H) were rooted to A/Goose/Guangdong/1/1996(H5N1). The viruses with names in colors were characterized in this study (the viruses isolated in Jiangxi province are colored red, and the viruses isolated in Hunan province are colored blue). Sequences of viruses with names in black were downloaded from available databases. Abbreviations are as follows: AB, aquatic bird; CK, chicken; CT, common teal; DCC, double-crested cormorant; DDK, domestic duck; DK, duck; ENV, environment; GS, goose; MD, mallard; QA, quail; RS, ruddy shelduck; RT, ruddy turnstone; TK, turkey; VS, velvet scoter; WB, wild bird; WS, whistling swan; SW, swan; WD, wild duck; AnH, Anhui; ALB, Alberta; CA, California; JX, Jiangxi; HeB, Hebei; HuN, Hunan; HK, Hong Kong; In-Alaska, interior Alaska; NJ, New Jersey; R- of Georgia, Republic of Georgia; RZ, Ri Zhao; ZJ, Zhejiang; SH, Shanghai; GD, Guangdong. Groups labeled with a red “#” in the phylogenetic trees of the six internal genes contain viruses of only the H10N8, H7N9, and H9N2 subtypes, and the human H10N8 isolate is indicated with a red arrow; 96% sequence identity cutoffs were used to categorize each gene segment in the phylogenetic trees.