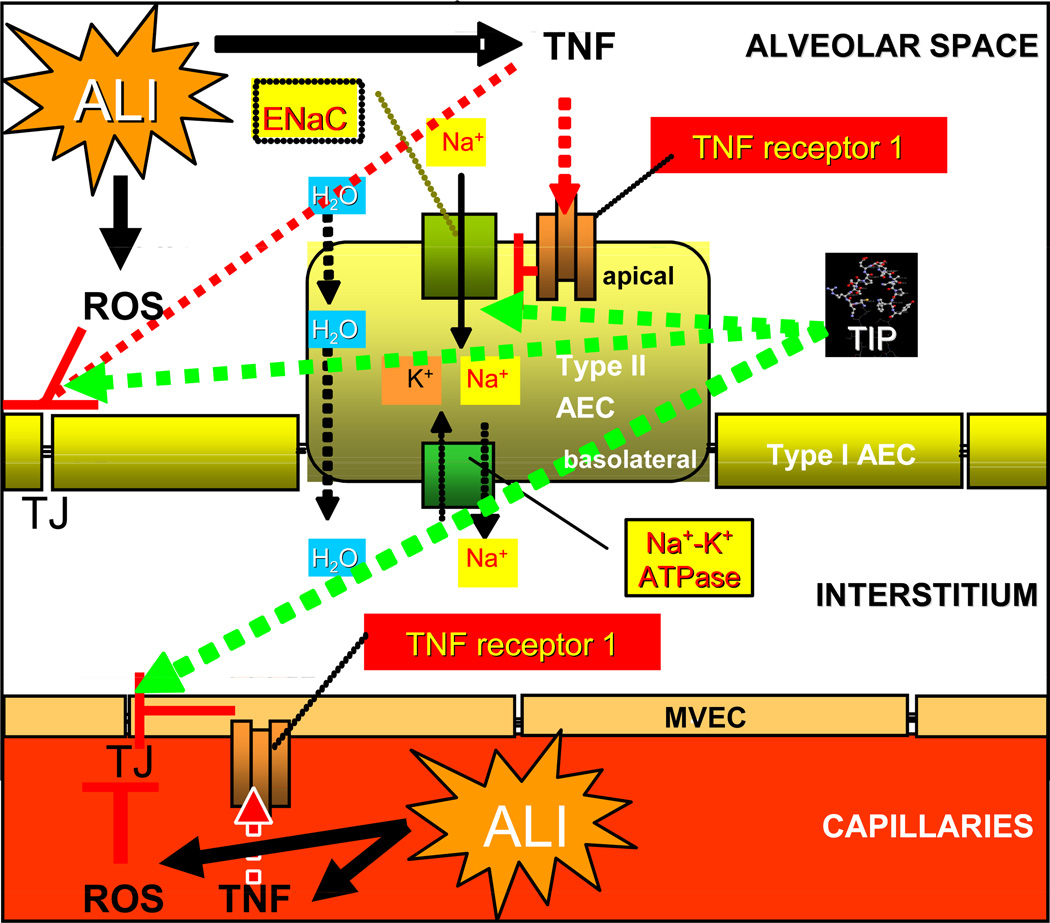
Scheme 2.
Dichotomous activity of TNF in alveolar liquid clearance and barrier protection during ALL TNF, which is induced during ALI, causes a downregulation of ENaC expression in type II alveolar epithelial cells, upon activating TNF-R1 [55, 56]. Moreover, TNF increases permeability, by means of interfering with tight junctions (TJ) in both alveolar epithelial (AEC) and capillary endothelial cells (MVEC). ROS, the generation of which is frequently increased during ALI, were also shown to downregulate ENaC and Na+-K+-ATPase expression [53] and moreover also lead to decreased endothelial barrier integrity. The TIP peptide, mimicking the lectin-like domain of TNF, is able to increase sodium uptake in alveolar epithelial cells and to restore endothelial barrier integrity, as such providing a significant protection against the development of permeability edema (red lines: inhibition, green arrows: activation).