Figure 1.
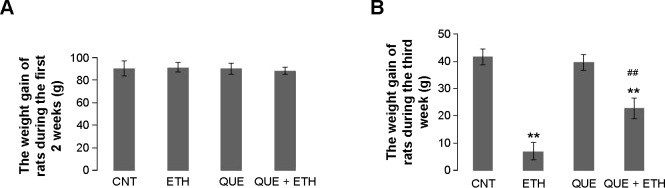
Quetiapine alone had no effect on weight gain of rats, but coadministration of quetiapine mitigated the decrease in body weight gain caused by ethanol.
Notes: Rats were given quetiapine (IP) or the vehicle of it for 3 weeks. During the 3rd week, they were given 20% ethanol (2 g/kg/day, IP) or equal volume of sterilized saline (IP) once a day. The body weight of rats was scaled every other 2 days. All groups showed comparable weight gains during the first 2 weeks (A). During the 3rd week, the ethanol administration significantly reduced the weight gain of rats. But this effect was effectively and significantly ameliorated by coadministration of quetiapine (B). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. **P<0.01 (ETH versus CNT); ##P<0.01 (QUE + ETH versus ETH).
Abbreviations: CNT, controls; ETH, ethanol; IP, intraperitoneal; QUE, quetiapine; QUE + ETH, quetiapine plus ethanol; SEM, standard error of mean.
