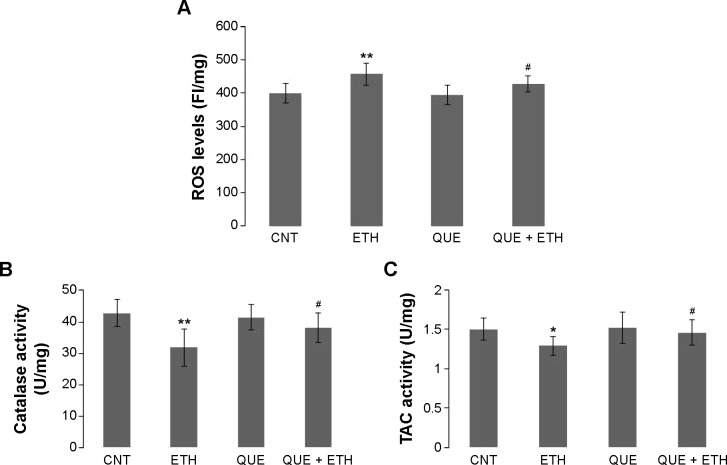
Figure 3.
Coadministration of quetiapine protected rats against the ethanol-induced changes in redox status in PFC.
Notes: (A) Quetiapine prevented the ethanol-induced increase in ROS in PFC; (B) Quetiapine prevented the ethanol-induced decrease in catalase activity in PFC; (C) Quetiapine prevented the ethanol-induced decrease in TAC in PFC. Rats were killed by decapitation. Their brains were quickly removed and the PFC tissue samples were processed for biochemical analyses. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (compared to CNT); #P<0.05 (QUE + ETH versus ETH).
Abbreviations: CNT, controls; ETH, ethanol; FI, fluorescence intensity; QUE, quetiapine; PFC, prefrontal cortex; QUE + ETH, quetiapine plus ethanol; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SEM, standard error of mean; TAC, total antioxidant capacity.