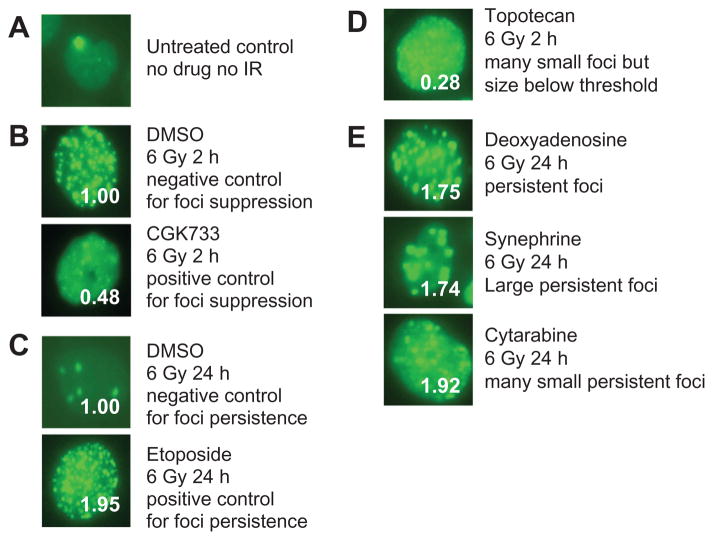
Figure 3.
Patterns of foci modification. A) Most untreated cells typically have zero to two foci, with occasional cells with a higher number of foci. B) (Upper) The negative control for foci formation at 2 hours was exposure to 1-hour pretreatment with 0.5% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (vehicle), irradiation with 6 Gy, and imaging 2 hours post-ionizing radiation (IR). The resulting mean foci count was given a value of 1.00 for reference at the 2-hour time point. (Lower) A positive control for agents mediating suppression of foci formation is the ataxia telangiectasia-mutated (ATM), ATM- and RAD3-related (ATR) inhibitor CGK-733. At 2 hours after 6 Gy, CGK-733 yielded a value of 0.48, or 48% of 2 hours of negative control. C) (Upper) A negative control for foci persistence at 24 hours was exposure to 1 hour of pretreatment with 0.5% DMSO (vehicle), irradiation with 6 Gy, and imaging 24 hours post-IR. The foci count was assigned a value of 1.00. (Lower) As a positive control for agents promoting enhanced foci persistence, the topoisomerase inhibitor etoposide was used. etoposide yielded a score of 1.95 at 24 hours post-6 gy. D) Pretreatment with topotecan 1 hour before the 6 gy dose and imaging at 2 hours yields many very small foci that fall below the software threshold, giving an artifactual value of 0.28 for foci number. E) Hits that scored >1.5 in the screen for enhanced foci persistence displayed a range of foci phenotypes. Deoxyadenosine (1.75) foci appeared similar to control foci but in greater numbers, synephrine (1.74) foci were comparatively less abundant but proportionately larger and brighter, and cytarabine (1.92) yielded many small, persistent foci.