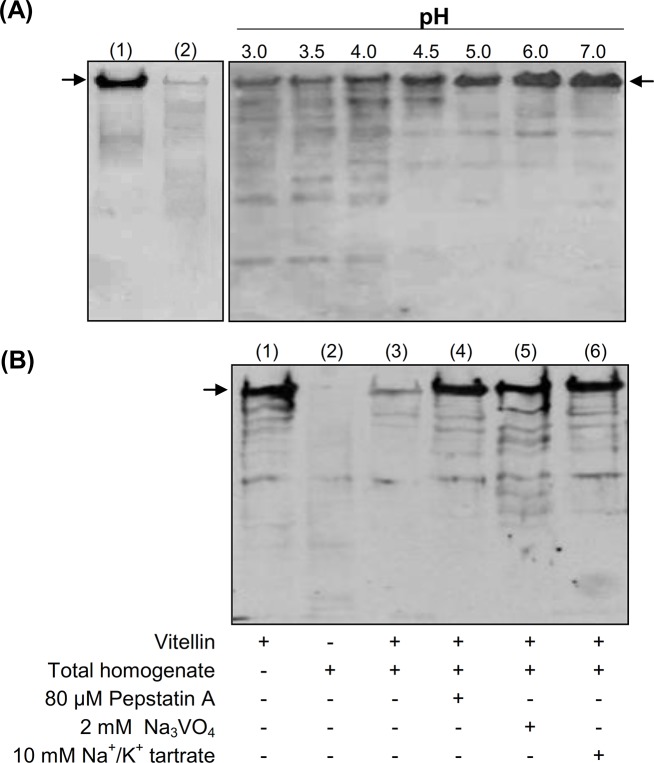
Fig 8. pH dependence and effect of DmCatD and acid phosphatase inhibitors on vitellin (Vt) proteolysis.
Homogenates from atretic ovaries were used as the enzyme source and purified Vt as substrate. (A), left panel, purified Vt and homogenates of ovarian tissues without incubation (lane 1 and 2, respectively). Right panel, in vitro pH dependence of Vt proteolysis. The reaction was carried out for 12 h at 37°C in different reaction buffers, according to the pH evaluated (3.0 to 7.0). In all cases, Vt degradation was evidenced by western blot using an anti-Vt antibody, after fractionation of proteins by 7.5% SDS-PAGE. (B), Vt and ovarian homogenates were incubated for 12 h at 37°C in a reaction medium at pH 4.0 either in the absence (lane 3) or in the presence of pesptatin A (inhibitor of aspartic peptidases, lane 4), Na3VO4 (inhibitor of tyrosine phosphatases, lane 5) or Na+/K+ tartrate (a broad spectrum phosphatase inhibitor, lane 6). Purified Vt and ovarian homogenate (lanes 1–2, respectively) were incubated in the same conditions and showed as controls. The arrows in the panels indicate the main subunits of purified Vt (Mr ~170 kDa and 174 kDa) visualized as a single immunoreactive band.