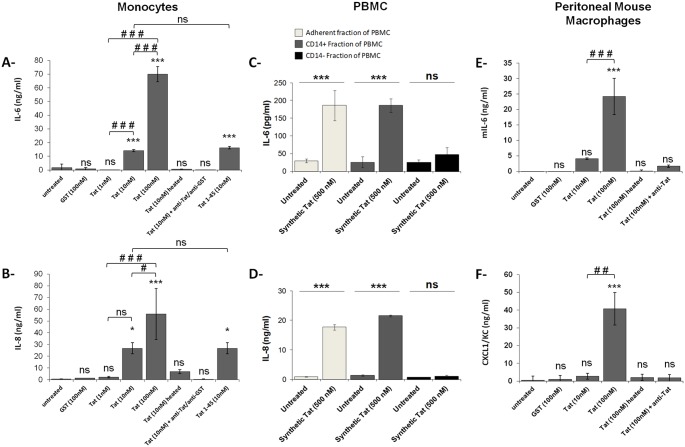
Fig 1. HIV-1 Tat induces IL-6 and IL-8 production in monocytes/macrophages.
(A-B) and (C-D) Human monocytes (0.5x106) or (E-F) Wt peritoneal mice macrophages (0.5x106) were incubated with increasing amounts of recombinant GST-Tat 1–101 protein (Tat), a deleted mutant GST-Tat 1–45 protein carrying the first 45 amino acid (Tat 1–45) or an equal amount of GST protein alone (GST). Untreated cells were used as negative controls. Tat heat-inactivated for 20 min at 95°C or Tat previously incubated with mAb anti-Tat for 60 min at 37°C, or GST were used for the control of the specificity. (C-D) Monocytes were isolated from PBMC using either adherence protocol as described in Material and Methods, or positive selection using CD14 MicroBead according to the manufacturer instruction (Miltenyi Biotec), CD14 negative fraction of PBMC was used as control. Cells were either kept untreated or treated with Synthetic Tat. After 24 h of treatment, human or mouse IL-6 and human IL-8 and mouse CXCL1/KC cytokines were measured in the culture supernatants by ELISA. Cytokine production is expressed in ng/ml. The data represent means and standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments. Asterisks represent P values comparing "untreated" group versus "Treated (as indicated)" group * for p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, ns non significant. Statistical significance comparing different group linked with a black line above the compared bar and are denoted with # for p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001, ns non significant.