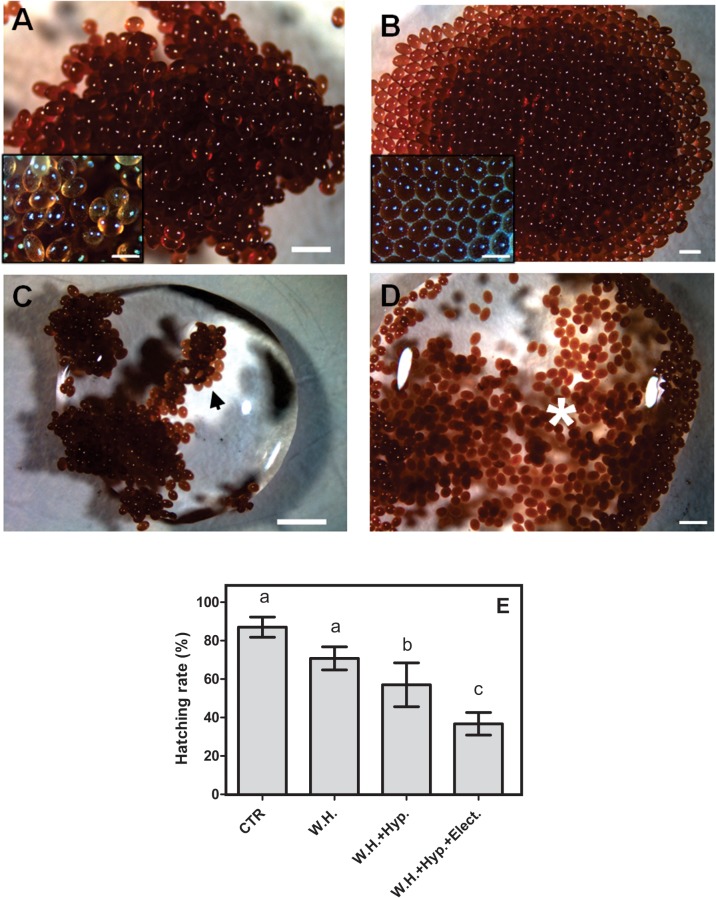
Fig 1. De-waxing of eggs using heptane and hypochlorite.
The eggs, in different treatment, were observed using stereomicroscope as indicated in the figure. To remove the egg wax coating, 10-mg egg batches were treated with ~40–50 μL of heptane for ~15 min as described. A = unaltered egg clump, B = monolayer of treated eggs, C = clump of unaltered eggs floating on top of aqueous droplet (white arrowhead), D = de-waxed eggs submerged in the aqueous droplet (white asterisks sign). E = the hatching rate of eggs in different treatments, unaltered eggs (CTR), with heptane (W.H.), with heptane and hypochlorite (W.H. + Hyp.) and with heptane, hypochlorite and electroporated (W.H.+ Hyp.+elect). Magnification bars: A-D: 2000 μm, Insert: 500 μm. Statistical analysis was carried out using the ANOVA and posttest Tukey (p<0.05), (Triplicate; n = 3).