Fig. 4.
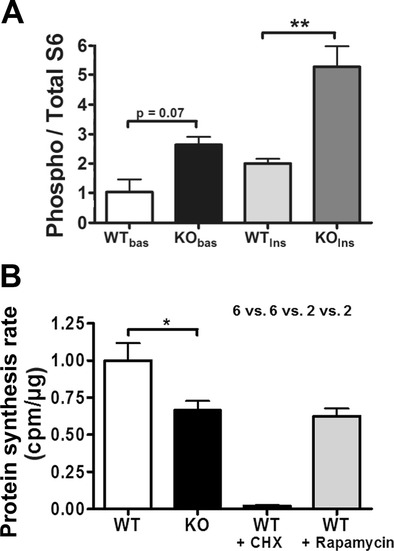
Ataxin-2 effects on global translation regulation and activity. a The ratio of ribosomal S6 phosphorylation normalized to total S6 content increased in Atxn2 −/− cells. MEF cells from WT or KO animals were serum-starved for 24 h, and S6 phosphorylation was measured at basal condition (bas) or after incubation with insulin (Ins) over 10 min. A trend towards increased S6 phosphorylation was observed in KO MEFs at basal condition after starvation, and a highly significant increase of S6 phosphorylation was measured after insulin treatment (n = 2–3 MEF lines per genotype). b ATXN2 deficiency reduced basal mRNA translational activity. The incorporation of [S35]-labelled methionine/cysteine was quantified in MEFs to assess global protein synthesis rates. Cycloheximide (CHX) or rapamycin were applied 90 min prior to labelling to some cell lines. KO MEFs showed a reduction in protein synthesis by 34 % in comparison to WT MEFs (n = 6 MEF lines per genotype in 3 independent technical replicates). As control and comparison, the translation elongation inhibitor CHX diminished translation to 2 %, the mTOR pathway inhibitor rapamycin to 63 % (n = 2 MEF lines)
