Figure 1. The NMD pathway influences differentiation decisions.
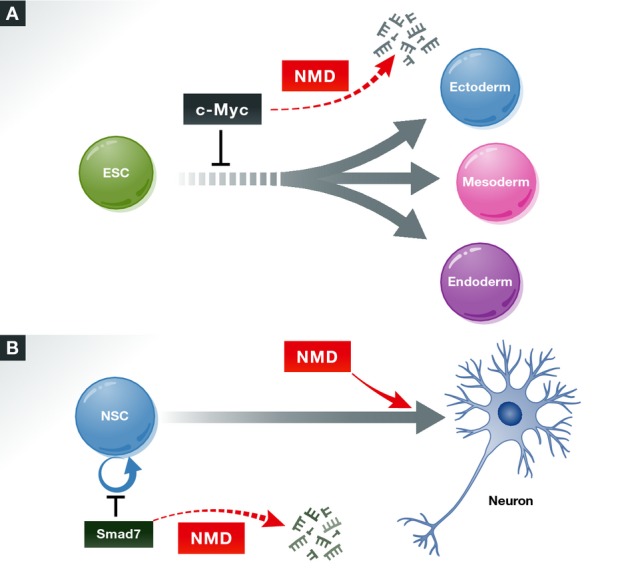
(A) NMD promotes the differentiation of embryonic stem cells (ESCs) into the three primary germ layers, in part, by promoting the decay of c-mycmRNA, which encodes an anti-differentiation/pro-proliferation factor (Li et al, 2015). (B) NMD factors have complex effects on the differentiation of neural lineage cells. The central NMD factor, UPF1, inhibits the differentiation of neural stem cells through its ability to promote the decay of the mRNA encoding the pro-neural differentiation factor SMAD7 (Lou et al, 2014). A NMD factor required for normal human cognition—UPF3B—appears to promote neural precursor differentiation and is required for neural maturation (Jolly et al, 2013).
