Figure 1.
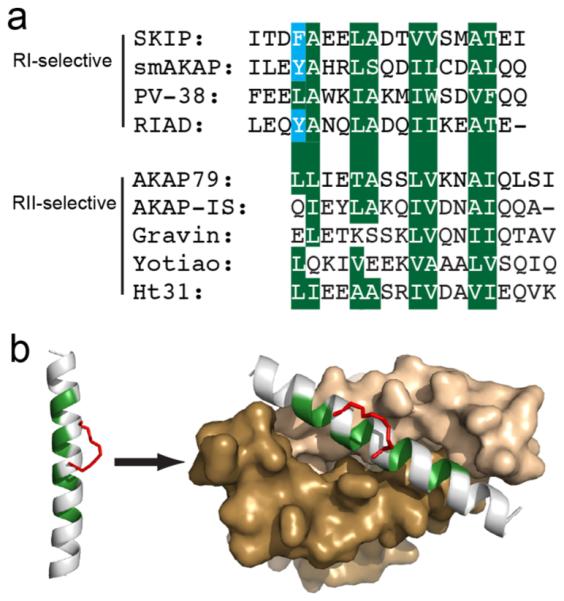
RIAD serves as a template for developing stapled RI-anchoring disruptors. (a) Alignment of various RI- and RII-specific AKAP or AKAP-mimicking sequences. The four hydrophobic registers shared by the docking sequences are highlighted in green. The aromatic residues shared by RI-specific sequences are highlighted in blue. (b) The hydrophobic surface of the α-helical docking peptide is highlighted in green. The hydrocarbon staple is introduced on the solvent-exposed surface and is shown in red. The right panel models the stapled peptide bound to the surface of the docking/dimerization (D/D) domain of PKA-RI (brown and tan) with its hydrophobic surface highlighted in green. The structure was rendered in PyMol using PDB ID 3IM4.
