Figure 2.
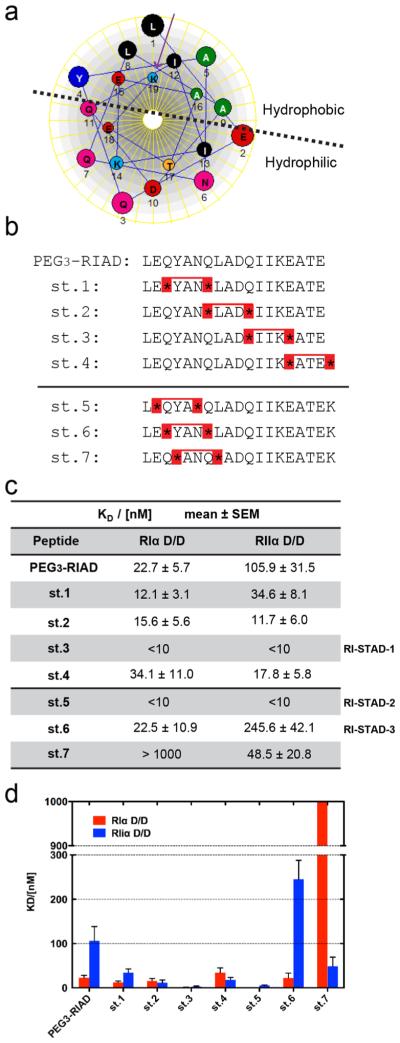
Development of RI-STAD peptides. (a) The amphipathic RIAD sequence is represented as a helical wheel. The addition of a terminal Lys (K19) is included in the wheel (as indicated by a purple arrow). The helical wheel was created using DNASTAR. (b) Sequences for two generations of peptide candidates are listed. The second-generation peptides, st.5–st.7, contain the addition of a terminal Lys residue. S5 is represented by asterisk symbol, and a red bridge represents the staple. (c) Fluorescence polarization (FP) was used to determine the dissociation constant of the fluorescein-labeled peptides using D/D domain constructs from either PKA-RIα or PKA-RIIα. Dissociation constants were calculated using nonlinear regression and are presented as the mean ± SEM from triplicate experiments. (d) Graphic presentation of the dissociation constants from the FP binding assay.
