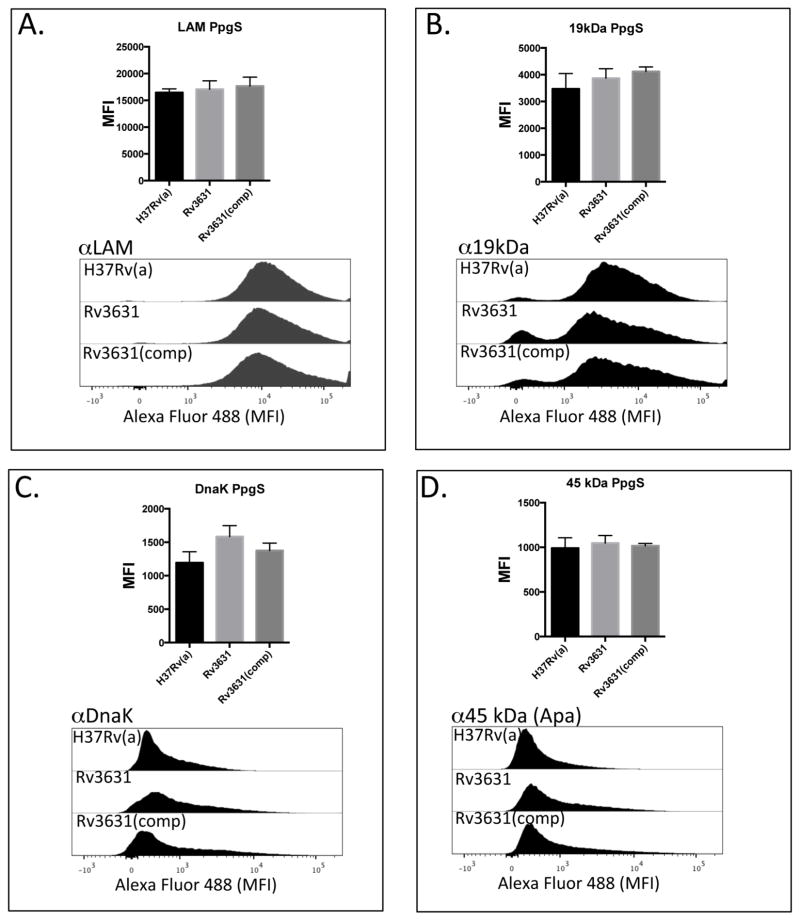
Figure 6. Surface exposure of DC-SIGN ligands by the WT and GalN-deficient mutants.
WT Mtb strains when compared to their corresponding Rv3631 (Panels A–D) and Rv3779 (Panels EH) GalN-deficient Mtb mutants display similar levels of the DC-SIGN ligands ManLAM, 19 kDa antigen, DnaK, and Apa (45 KDa antigen) as their WT counterparts as determined by the similar extent of MoAb binding to their cell surfaces. Complementation of these mutations ((Rv3631(comp) and Rv3779(comp)) also had no significant effect on surface availability. Intact irradiated Mtb strains were labeled identically with previously titrated MoAbs against the above DC-SIGN ligands followed by extensive washing of unbound MoAb. MoAb-bound bacteria were counterstained with a secondary Alexa-Fluor 488-conjugated anti-mouse IgG, followed by washing and geometric MFI determined by flow cytometry. The bar graph on the top of each histogram set represents the result of a total of 3 separate experiments. (“PpgS” refers to the polyprenyl-phospho-N-acetylgalactosaminyl synthase strain comparisons and “GT” refers to the galactosaminyl transferase strain comparisons.) P values for all experiments were > 0.150.