Figure 3. Bivalent binding to the Arf1 GTPase by the AP-1, COPI, and Exomer cargo adaptors.
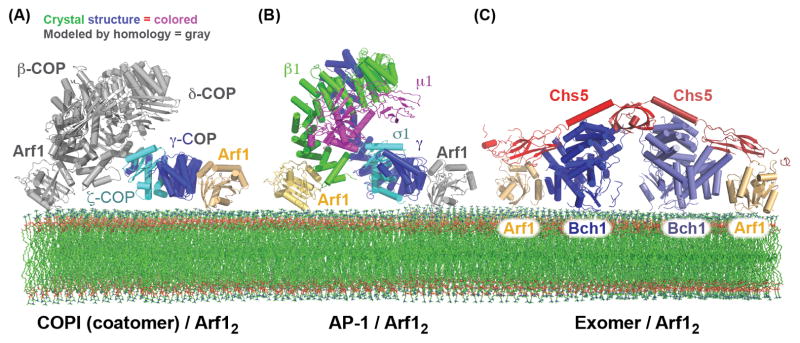
(A) Structural model of the COPI F-subcomplex recruited to the membrane surface by two molecules of Arf1. The Arf1 molecule and portions of the F-subcomplex shown in gray are modeled based on homology to the AP-2 complex, and homology between the β-COP and γ-COP subunits (the observed and modeled Arf1 interactions were confirmed biochemically) [61]. It should be noted that a recent cryo-EM study of the COPI coat suggested that the F-subcomplex may adopt a different conformation than does the AP-2 core [112]. (B) Structural model of the AP-1 core complex recruited to the membrane surface by two molecules of Arf1. The Arf1 molecule shown in gray is modeled based on homology between the β1 and γ subunits (the observed and modeled Arf1 interactions were confirmed biochemically) [71]. (C) Structure of the Exomer/Arf1 complex bound to membranes (all interactions, including with the membrane surface, were confirmed biochemically) [88].
