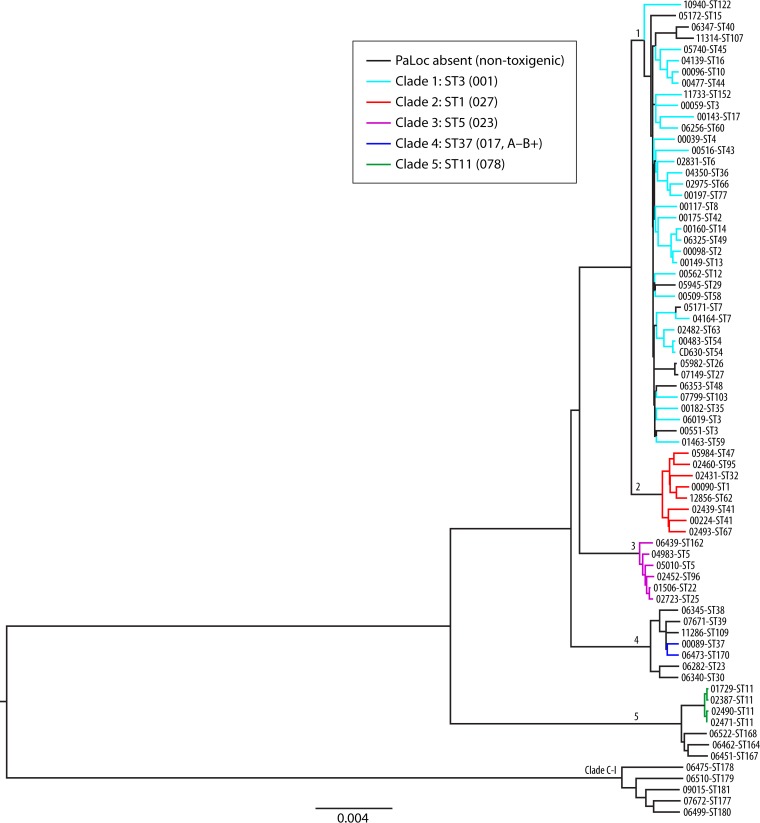
FIG 2.
Phylogenetic tree showing representatives of six currently described C. difficile clades and the relationship between toxigenic and nontoxigenic isolates. A maximum likelihood tree was generated from the alignment of 1,426 core genes of 73 C. difficile isolates. Isolates represented extremes of clinical severity, geographic diversity, and toxigenic status. Clades are indicated by their designated number. Nontoxigenic isolates are indicated by black branches. Toxigenic isolates are indicated by branches colored according to clade. The ST and RT (in parentheses) of a well-characterized representative of each clade are indicated. (Reproduced from reference 107 by permission of the Society for Molecular Biology and Evolution.)