Fig. 3.
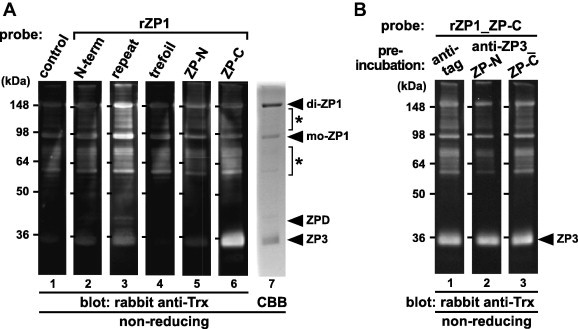
Far-Western blot analyses of the egg-coat proteins with the recombinant domains of ZP1. The egg-coat proteins were separated by SDS–PAGE under non-reducing conditions followed by electroblotting onto nitrocellulose membranes. (A) The blocked membranes were incubated with the control protein (lane 1), recombinant N-terminal (N-term), repeat, trefoil, ZP-N and ZP-C domains of ZP1 (rZP1s) (lanes 2–6, respectively; see Fig. 1) as Trx-tagged probes followed by immunostaining with rabbit anti-Trx antibody. The proteins in the SDS–PAGE gel were also stained with CBB (lane 7). (B) The blocked membranes were preincubated with the mouse anti-tag (lane 1), anti-ZP3_ZP-N and ZP-C antisera (lanes 2 and 3, respectively) being produced as described in Section 4 prior to the incubation with the recombinant ZP-C domain of ZP1 (rZP1_ZP-C), and immunostained with rabbit anti-Trx antibody. Migration positions of dimeric (di-) and monomeric (mo-) ZP1, ZPD and ZP3 (arrowheads), and the previously-reported anti-ZP1 positive proteins (asterisks) are shown on the right. Molecular weights (kDa) are indicated on the left.
