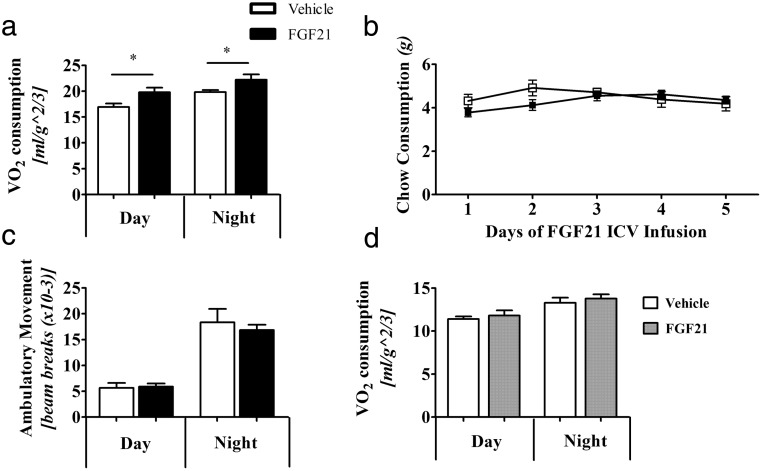
Figure 2.
A low central FGF21 dose of 0.4 μg/d into WT mice causes an increase in O2 consumption. Mice (n = 8 per group) administered icv-FGF21 have a higher metabolic rate of VO2 (A), yet do not consume more food (vehicle, n = 8, FGF21, n = 7) (B) or have increased activity ambulatory activity (n = 14 per group) (C). Mice given the circulation-matching, 1.6-μg/d sc-FGF21 dose (vehicle, n = 6, FGF21 n = 8) do not show an increase in VO2 consumption (D). Graphs are shown ± SEM. *, P < .05; **, P < .01; by Student's t test, food consumption not significant by repeat measures ANOVA, P = .3193.