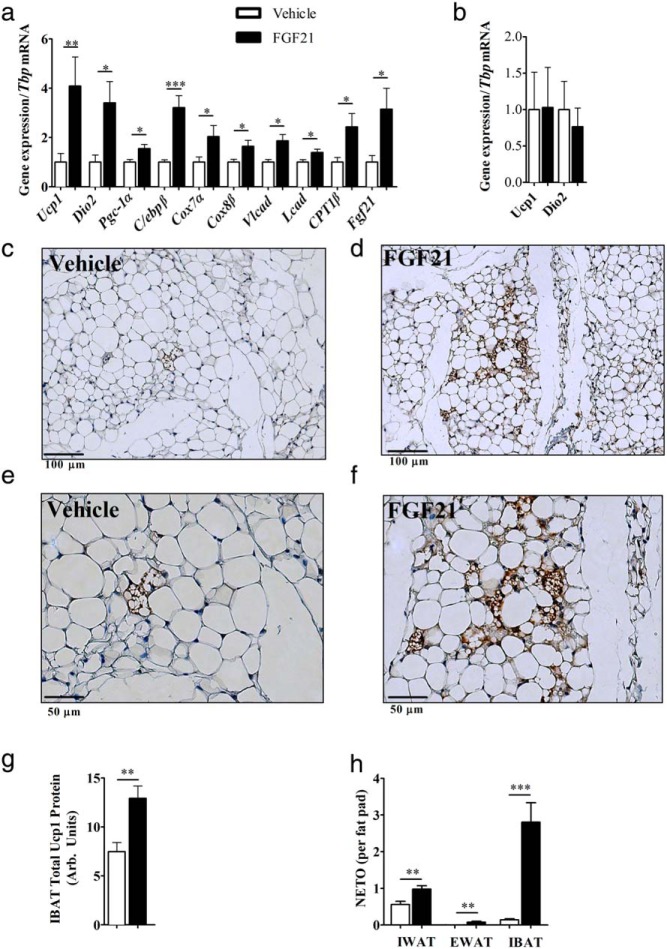
Figure 3.
Browning profile of inguinal adipose tissue, Ucp1 protein expression in BAT, and NETO in adipose depots: icv-FGF21 (0.4 μg/d) 5-day infusion into mice (n = 15 per group) causes increases in expression of BAT-specific markers and markers of thermogenesis and fatty acid oxidation in IWAT (A), whereas a circulation-matching sc-FGF21 dose (1.6 μg/d) (n = 7 per group) fails to induce expression of Ucp1 or Dio2 after 5 days of treatment (B). Histologic examinations (vehicle, n = 8, FGF21, n = 7) of IWAT revealed that 5-day icv-FGF21 administration (0.4 μg/d) caused increased protein expression of Ucp1 as assessed immunohistochemistry (C–F). IBAT total Ucp1 protein is increased after 5-day icv-FGF21 (0.4 μg/d)-treated mice (vehicle, n = 7, FGF21, n = 6) (G). NETO increased after a 5-day icv-FGF21 administration in IWAT (vehicle, n = 16, FGF21 n = 19), EWAT (vehicle n = 16, FGF21, n = 20), and IBAT (vehicle, n = 17, FGF21, n = 20) (H). Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1b (Cpt1β). Graphs are shown as mean ± SEM. *, P < .05; **, P < .01; ***, P > .001 by Student's t test.