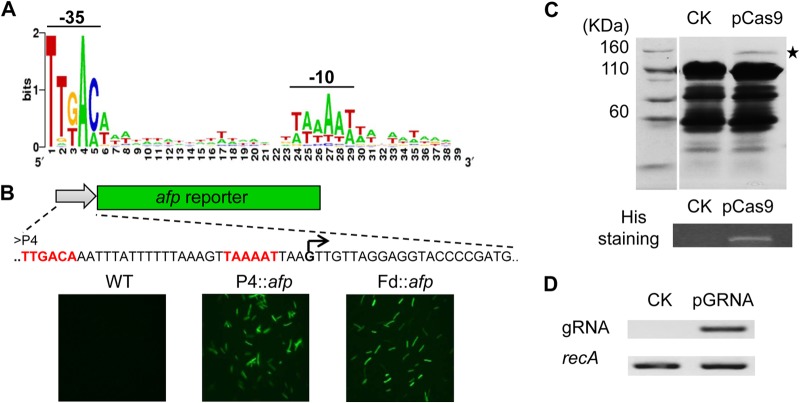
FIG 1.
Generation and validation of Cas9 expression system. (A) Alignment of predicted σA-dependent promoters from C. cellulolyticum. Two highly conserved regions (−35 and −10) are separated by a 17-nt T/A-rich spacer. (B) Promoter activity test, in which synthetic promoter P4 drives an anaerobic florescent protein-encoding gene (afp). The right-angled arrow indicates the potential transcriptional start site. The −35 and −10 regions are in red. Fluorescence microscopy of C. cellulolyticum wild type (WT) and transformants carrying P4::afp or Fd::afp constructs. (C) SDS-PAGE analysis of whole-cell proteins from transformants with empty vector (CK) and pCas9. The star denotes the estimated Cas9 band. The full-length His-tagged Cas9 is further verified by His protein staining. (D) RT-PCR analysis of gRNA in both CK and pGRNA strains, using the recA gene as an internal calibrator.