FIG 4.
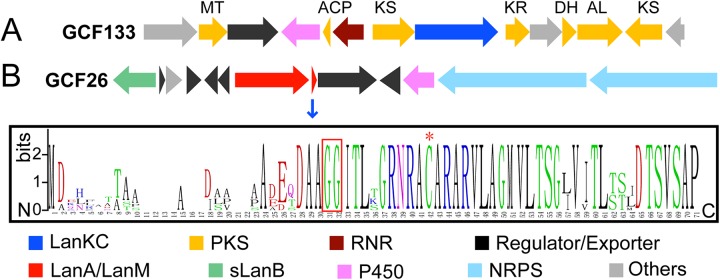
Association of genes encoding lanthipeptide synthetases with PKS and NRPS genes. (A) A representative gene cluster of GCF133 that likely encodes lanthipeptide synthetase-PKS hybrid systems. (B) A representative gene cluster of GCF26 that likely encodes lanthipeptide synthetase-NRPS hybrid systems, and a logo depicting the precursor peptide sequences. The empty sites in the leader peptide region are a consequence of high sequence divergence (i.e., no conserved residues). The sequence alignment of GCF26 precursor peptides is shown in Fig. S5 in the supplemental material. The GG leader peptide cleavage site and the conserved Cys residue in the putative core region are highlighted by a red box and a red asterisk, respectively. The putative functions of gene products are shown by colors. MT, malonyl transferase; ACP, acyl carrier protein; KS, ketosynthase; KR, ketoreductase; DH, dehydratase/enoyl-CoA hydratase; AL, ATP-dependent ligase; RNR, ribonucleotide reductase-like (these RNR-like proteins appear to contain the ligands for a dinuclear metal cluster but not a tyrosine for radical formation); sLanB, small LanB. The boundaries of each gene cluster are predicted based on the conserved genes within each GCF and are not clearly defined.
