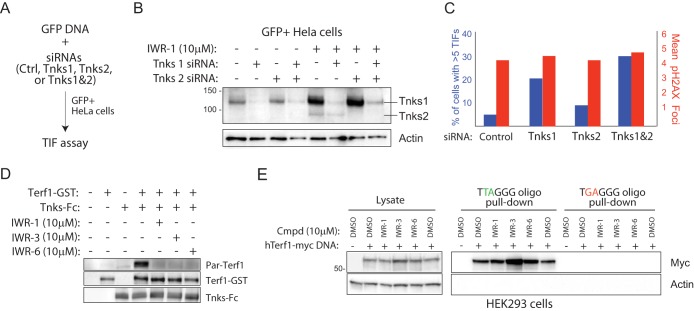
FIG 5.
Chemical disruption of Tnks likely results in increased parsylation-dependent Terf1 binding to telomeric DNA. (A) Strategy for isolating HeLa cells transfected with Tnks1 and/or Tnks2 siRNA. A plasmid supporting constitutive expression of GFP is cotransfected with a pool of siRNAs (4 individual siRNAs per gene) targeting either Tnks1, Tnks2, or both into HeLa cells. GFP+ HeLa cells isolated by flow cytometry were analyzed for levels of TIF 24 h later. (B) Biochemical evidence for on-target effects of Tnks siRNA pools in GFP+ HeLa cells. GFP+ cells presumably harboring the indicated Tnks siRNA pools were isolated by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) and then subjected to Western blot analysis following culturing in the presence/absence of IWR-1 for 24 h. IWR-1 was used here to aid in the visualization of relative Tnks protein abundance in siRNA-treated/untreated cells. (C) Quantification of TIF in GFP+ HeLa cells transfected with the indicated siRNA pools as described for panel B. (D) IWR-1, -3, and -6 inhibit Tnks-mediated parsylation of Terf1 in vitro. Tnks1-Fc fusion protein purified, using protein A-Sepharose, from HEK293 cells transiently transfected with Tnks1-Fc DNA was incubated with recombinant Terf1-GST protein, NAD-biotin (2.5 μM), and the indicated compounds (5 μM). (E) Tnks inhibitors increase Terf1 binding to telomeric repeat sequences. HEK293 cells transfected with a human Terf1-myc (hTerf1-myc) or control DNA were treated with the indicated compounds for 36 h prior to lysing. The lysate was incubated with biotinylated oligonucleotides containing 5 copies of Terf1-binding or mutated telomeric repeat sequence and streptavidin-coated Sepharose. The starting material and oligonucleotide-bound protein were subjected to Western blot analysis.