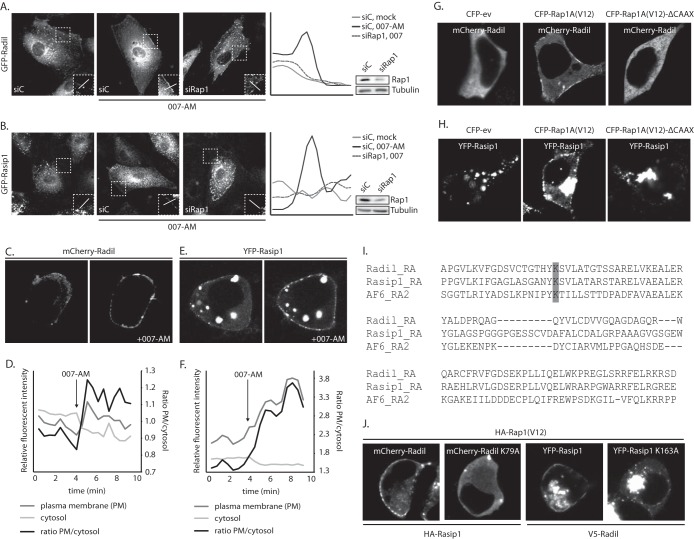
FIG 2.
Active Rap1 recruits Radil and Rasip1 to the plasma membrane. (A) The left panel shows live imaging of confluent monolayers of HUVECs infected with a lentivirus transducing GFP-Radil and treated with control siRNA (siC) or siRNA targeting Rap1A and Rap1B (siRap1). The cells were imaged prior to or 15 min after stimulation with 007-AM. The boxed areas of cell-cell contacts are enlarged in the insets. In the right panel, a graph shows the relative intensity profiles of fluorescent signal intensities along the line scans depicted in the boxed area. The knockdown efficiency was assessed by Western blotting. (B) The left panel shows live imaging of confluent monolayers of HUVECs infected with a lentivirus transducing GFP-Rasip1 and treated with control siRNA (siC) or siRNA targeting Rap1A and Rap1B (siRap1). The cells were imaged prior to or 15 min after stimulation with 007-AM. The boxed areas of cell-cell contacts are enlarged in the insets. In the right panel, a graph shows the relative intensity profiles of fluorescent signal intensities along the line scans depicted in the boxed area. Knockdown efficient was assessed by Western blotting. (C) Still images (taken prior to and 3 min after 007-AM stimulation) corresponding to the live imaging (see Movie S2 in the supplemental material) of HEK293T cells transiently transfected with HA-Epac1, HA-Rap1A, mCherry-Radil, HA-Rasip1, and HA-ArhGAP29. (D) Quantitative plasma membrane (PM)/cytosol analysis (as in Fig. 1F) of mCherry-Radil translocation in Movie 2 in the supplemental material. (E) Still images (taken prior to and 2 min after 007-AM stimulation) corresponding to the live imaging (see Movie S3 in the supplemental material) of HEK293T cells transiently transfected with HA-Epac1, HA-Rap1A, V5-Radil, YFP-Rasip1, and HA-ArhGAP29. (F) Quantitative plasma membrane (PM)/cytosol analysis (as in Fig. 1F) of the YFP-Rasip1 translocation shown in Movie S3 in the supplemental material. (G) Live imaging of mCherry-Radil in HEK293T cells transfected with mCherry-Radil, HA-Rasip1, and HA-ArhGAP29 and with either CFP-ev, CFP-Rap1A(V12) or CFP-Rap1A(V12)ΔCAAX. (H) Live imaging of YFP-Rasip1 in HEK293T cells transfected with YFP-Rasip1, V5-Radil, and HA-ArhGAP29 and with either CFP-ev, CFP-Rap1A(V12), or CFP-Rap1A(V12)ΔCAAX. (I) Alignment of the RA domains of Radil, Rasip1, and the second RA domain of AF6. Highlighted with gray is the conserved lysine, which is essential for interaction with GTP-loaded Rap1. (J) Live imaging of wild-type versus RA mutant mCherry-Radil (upper panels) and wild-type versus RA mutant YFP-Rasip1 (lower panels) in HEK293T cells transfected with HA-Rasip1, V5-Radil, HA-ArhGAP29, and HA-Rap1A(V12), together with mCherry-Radil, mCherry-Radil K79A, YFP-Rasip1, or YFP-Rasip1 K163A. The experiments were repeated at least three times; representative images are shown.