Fig. 3.
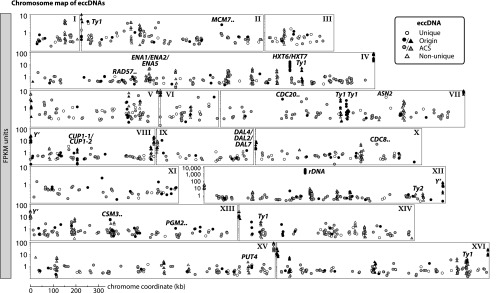
Genomic overview of eccDNA types detected in S. cerevisiae. Chromosomal map of S. cerevisiae eccDNA from Circle-Seq of 10 populations (R, Z, and S samples; see Fig. 2 legend). Highly conserved genes on eccDNAs are annotated, including genes that encode cell cycle regulators (CDC8 and CDC20), phosphoglucomutase (PGM2), a recombination repair protein (RAD57), and a helicase complex component (MCM7). Annotated also are genes encoding glucose, sodium, proline, and allantoin transporters HXT6, HXT7, ENA1, ENA2, ENA5, PUT4, DAL2, DAL4, and DAL7, as well as the asparagine synthetase gene ASN2, some retrotransposons (Ty elements) and telomeres with Y′ genes (see Dataset S1 for a list of all genes on eccDNAs). x axis, chromosomal coordinates for chromosomes I–XVI. (Scale bar, upper right.) y axis, logarithmic representation of normalization of each eccDNA to the number of mapped read fragments per kilobase from a million mapped reads (FPKM). Circles, unique eccDNA; triangles, nonunique eccDNA; black, eccDNAs with proposed replication origins or ARS sites; gray, eccDNAs with the ARS 17-bp consensus sequence (ACS); open circles and open triangles, eccDNAs without origin, ARS, and ACS; gene with two punctuation marks, more than one gene on the eccDNA. EccDNAs were annotated as unique if they included at least one uniquely mapped read to the reference genome and were annotated as nonunique if all included reads mapped equally well to several loci.
