Fig. S5.
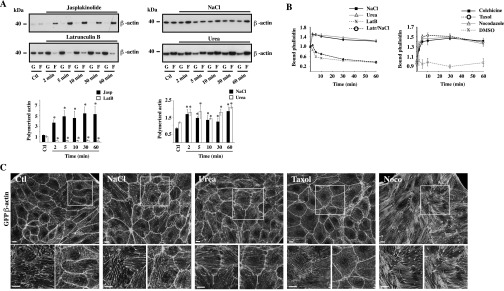
Actin remodeling by NaCl, urea, and chemicals that interfere with microfilament stability. (A) Time-dependent effects of jasplakinolide (0.4 µM), latrunculin B (2.5 µM), and NaCl and urea challenge (500 mOsmol/kg) on actin polymerization dynamics in LLC-PK1 cells were analyzed by Western blot. F-actin/G-actin ratios are shown below. Data depict fast effects by chemicals and hyperosmotic challenge. (B) TRITC-phalloidin fluorescence depicting increased actin polymerization in LLC-PK1 cells by NaCl challenge, urea challenge, and chemicals that interfere with MT polymerization. Latrunculin B, used as a control of actin depolymerization, strongly reduced actin polymerization by NaCl. Error bars show mean ± SEM from four independent experiments. *P < 0.05 vs. control. (C) Maximum projection of TRITC-phalloidin confocal z-stacks show actin organization under isotonic conditions (Ctl), after 30 min of NaCl or urea challenge (500 mOsmol/kg), and after the addition of taxol (10 µM, 30 min) or nocodazole (Noco) (10 µM, 30 min). Boxes below each image show enlarged maximum projections (Right) and an image of a single, basal confocal plane that depicts actin stress fibers (Left). (Scale bars: 5 µm.) Representative images from three independent experiments are shown.
