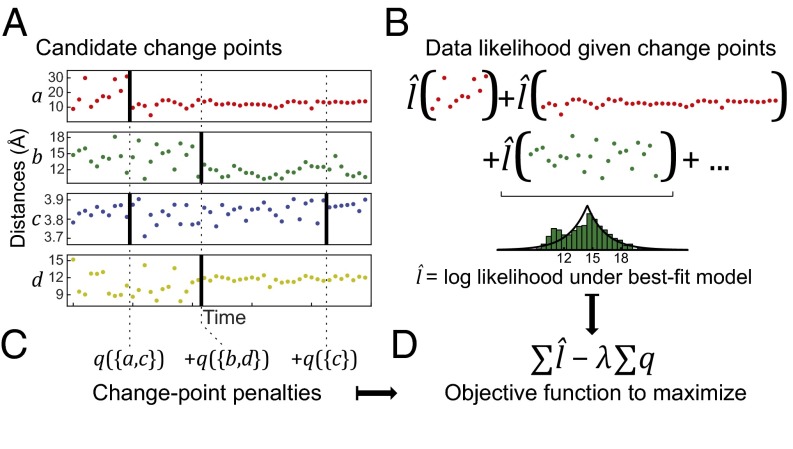
Fig. 1.
Given many noisy observables, the SIMPLE method detects change points for each one by maximizing a penalized-likelihood objective function that reflects the assumption that each change likely involves multiple observables. For (A) any candidate set of change points, (B) a statistical model is fitted to the data between each pair of change points in each observable, and the log-likelihood values are summed over all data segments and all observables. (C) A penalty for each set of simultaneous change points is summed over all change times. (D) The objective function is the total log-likelihood minus a sensitivity parameter, λ, times the total penalty.