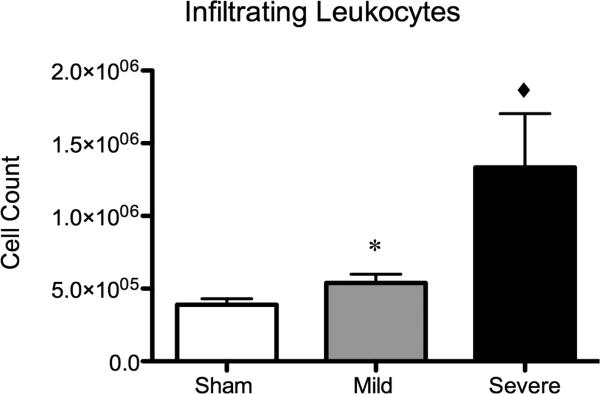
Figure 2. Severity of brain injury determines degree of peripheral leukocyte infiltration.
Mild TBI without any gross evidence of hemorrhage resulted in a significant increase in overall cell counts of peripheral leukocytes within the injured brain (*=p<0.05) as compared to sham injury. Severe injury, with grossly evident hemorrhage within the brain, resulted in a 3.4-fold increase in peripheral leukocytes within the injured brain (◆=p<0.001) as compared to sham injury.