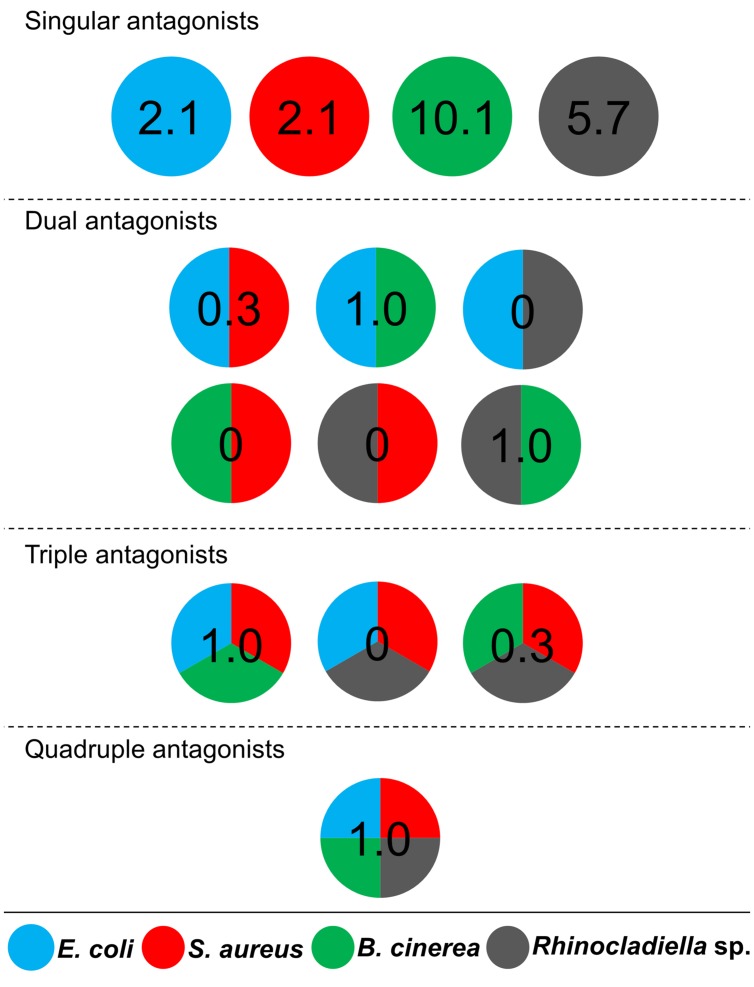
FIGURE 1.
Distribution of antagonistic bacteria isolated from multiple Lobaria pulmonaria thalli. Dual-culture experiments with 388 bacterial cultures were used to identify antagonists against four different model pathogens. Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus were used as models for human pathogens, Botrytis cinerea and Rhinocladoniella sp. were used as models for plant and lichen pathogens, respectively. Results are presented in a schematic illustration of antagonists, targeting a specific pathogen (indicated by relative numbers and different colors, respectively). Divided circles indicate particular combinations of pathogens, which were inhibited by an assigned percentage of Lobaria-associated isolates. Singular antagonists: Lobaria-associated isolates that inhibited only one model pathogen; Dual antagonists: isolates that inhibited two distinct model pathogens; Triple antagonists: isolates that inhibited three distinct model pathogens; Quadruple antagonists: isolates that inhibited four distinct model pathogens.