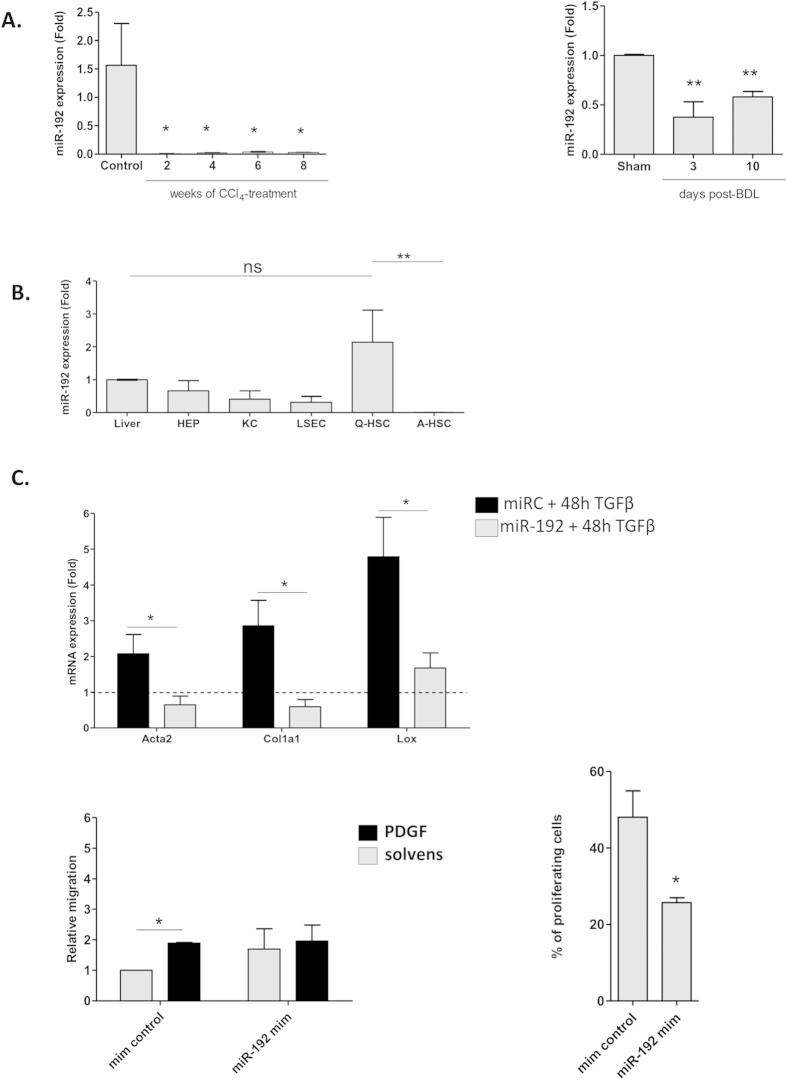
Figure 6. Expression and function of miR-192 in primary mouse HSCs.
(A) Expression of miR-192 in mouse HSCs during in vivo activation. Mir-192 expression levels were assessed in HSCs isolated from control mice, mice treated with CCl4 and from mice after BDL- or sham-operation at indicated time points after treatment or surgery. miRNA expression is shown relative to control or sham operated mice. (B) miR-192 expression in different hepatic cell types isolated from healthy mouse livers. MiR-192 expression was evaluated by qPCR in hepatocytes, quiescent and in vitro activated HSCs, KCs and LSECs. Mir-192 expression is shown relative to whole liver (C) Effect of miR-192 over-expression on cell activation, migration and proliferation in primary mouse HSCs. The contribution of miR-192 to HSC proliferation was evaluated in transfected mouse HSCs 1 day after miR-192 mimic transfection. HSCs were exposed to EdU, fixed 2 days later and stained for DNA-incorporated EdU. Proliferation is represented by the percentage of EdU-positive cells. Contribution of miR-192 on mouse HSC migration was assessed by a transwell migration assay on primary mouse HSCs transfected with mimic miR-192. PDGFbb (20 ng/mL) was added to promote cell migration. After 18 hours migrated cells were stained with DAPI and counted. Results are represented as migration relative to the non-PDGF stimulated cells. Finally, the effect of overexpressing miR-192 on cell activation was evaluated by exposing freshly isolated mice HSCs to TGFβ1 (10 ng/mL) or solvent for 48 hours. Results are represented as relative expression to miR control incubated with solvent.