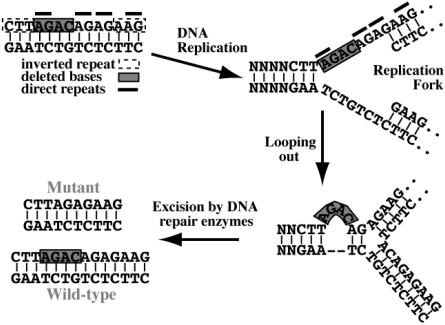
Figure 1.
Possible mechanism of the 4-bp deletion through slipped mispairing. At the replication fork, the second AG direct repeat can mispair with the complement of the first AG repeat, causing a loop on the upper strand that is excised by DNA repair enzymes. The resultant upper-strand copies will have the 4-bp deletion, whereas the lower-strand copies will be the wild-type sequence.