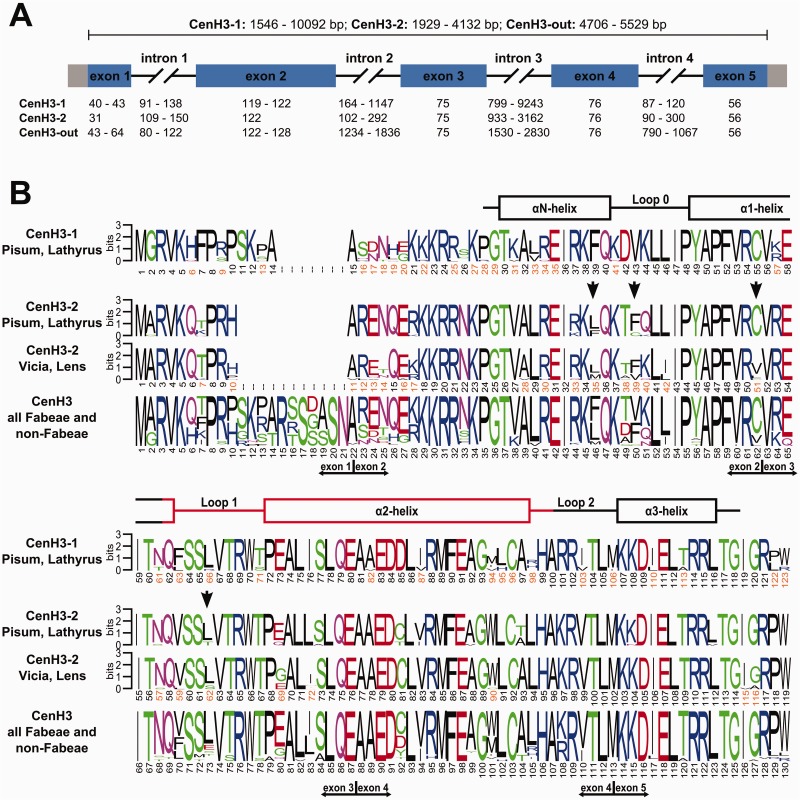
Fig. 5.
Structure and divergence of CenH3 genes and histones. (A) Schematic of CenH3 genes. The basic structure of the CenH3-1 and -2 genes is highly conserved, consisting of 5 exons (rectangles; coding regions are in blue) of conserved size and four introns of highly variable size (black lines). (B) Sequence logos calculated separately for CenH3-1 and CenH3-2 as well as for all CenH3 sequences used in this study. The secondary structure of the HFD is shown above the logos, as adopted from Tachiwana et al. (2011). The putative centromere targeting domain (CATD) is shown in red. Sites in CenH3-2 that were predicted to evolve under positive selection are marked with vertical black arrows.