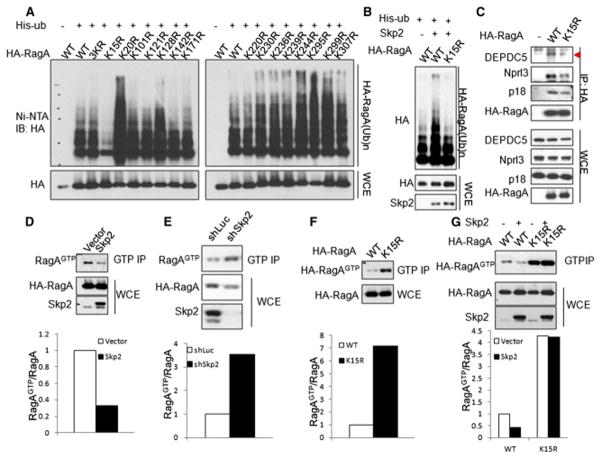
Figure 3. Skp2-mediated RagA-K15 ubiquitination recruits GATOR1 and inhibits RagA GTP binding.
(A) Screening for RagA ubiquitination sites. In vivo ubiquitination assay of RagA KR (lysine (K) mutated to arginine (R)) mutants. 3KR indicates the mutant with the lysine at residues 7, 8 and 9 mutated to arginine. (B) In vivo ubiquitination assay of WT RagA and RagA-K15R mutant by Skp2. (C) IP analysis of the interaction between WT RagA or RagA-K15R mutant and GAPTOR1 components (DEPDC5 and Nprl3) or Ragulator component p18 in HEK293T cells. Triangle indicates annotated protein. (D) GTP binding assay of RagA in empty vector and Skp2 overexpressed HEK293T cells. (E) GTP binding assay of RagA in control (shLuc) and Skp2 knockdown (shSkp2) HEK293T cells. (F) GTP binding assay of WT RagA and RagA-K15R mutant in HEK293T cells. (G) GTP binding assay of the WT RagA or RagA-K15R mutant in empty vector and Skp2 overexpressed HEK293T cells.