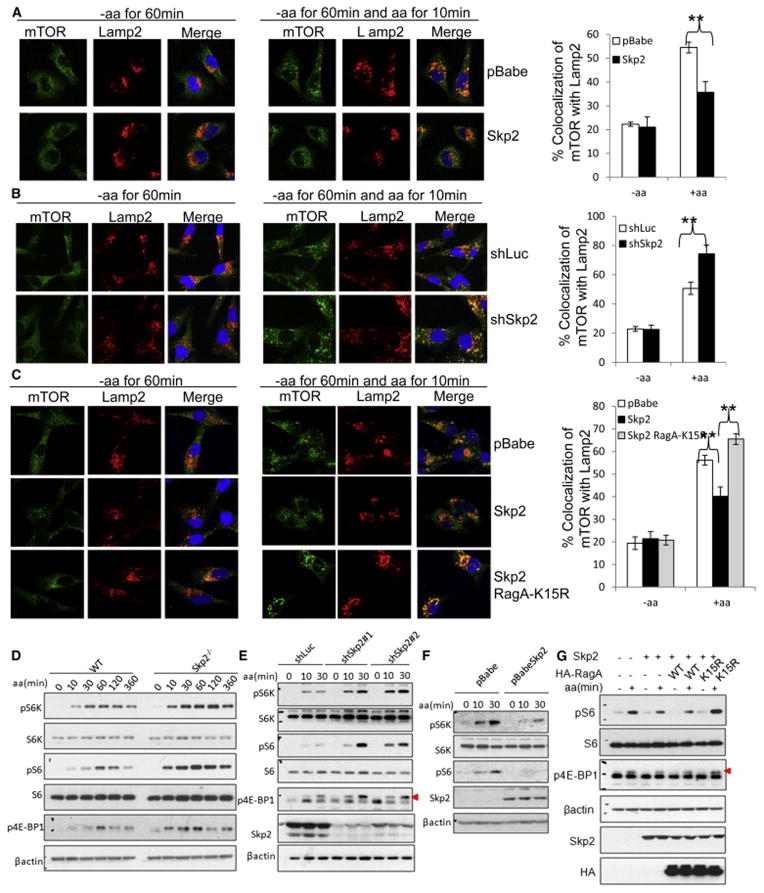
Figure 4. Skp2-mediated RagA-K15 ubiquitination negatively regulates amino acid-dependent mTORC1 lysosomal localization and activation.
(A) IF assay of amino acid-dependent co-localization of mTOR with lysosome marker Lamp2 in control (pBabe) and Skp2 overexpressed MDA-MB-231 cells. Quantitative data are represented as mean +/− S.D., (B) IF assay of amino acid-dependent co-localization of mTOR with lysosome marker Lamp2 in control (shLuc) and Skp2 knockdown (shSkp2) MDA-MB-231 cells. Quantitative data are represented as mean +/− S.D., ** indicates p<0.01. (C) IF assay of amino acid-dependent co-localization of mTOR with lysosome marker Lamp2 in MDA-MB-231 cells overexpressed with indicated proteins. Quantitative data are represented as mean +/− S.D., ** indicates p<0.01. (D) IB analysis of amino acid-dependent mTORC1 signaling in WT and Skp2−/− primary MEFs. (E) IB analysis of amino acid-dependent mTORC1 signaling in control (shLuc) and Skp2 knockdown (shSkp2) MDA-MB-231 cells. Triangle indicates annotated protein. (F) IB analysis of amino acid-dependent mTORC1 signaling in MDA-MB-231 cells transfected with indicated vectors. (G) IB analysis of amino acid-dependent mTORC1 signaling in the cells overexpressed with indicated proteins. Triangle indicates annotated protein. Cells in (A–G) were starved for amino acids for 1 hour and restimulated with amino acids for indicated time before lysis. See also Figure S3 and S4.