Fig. 3.
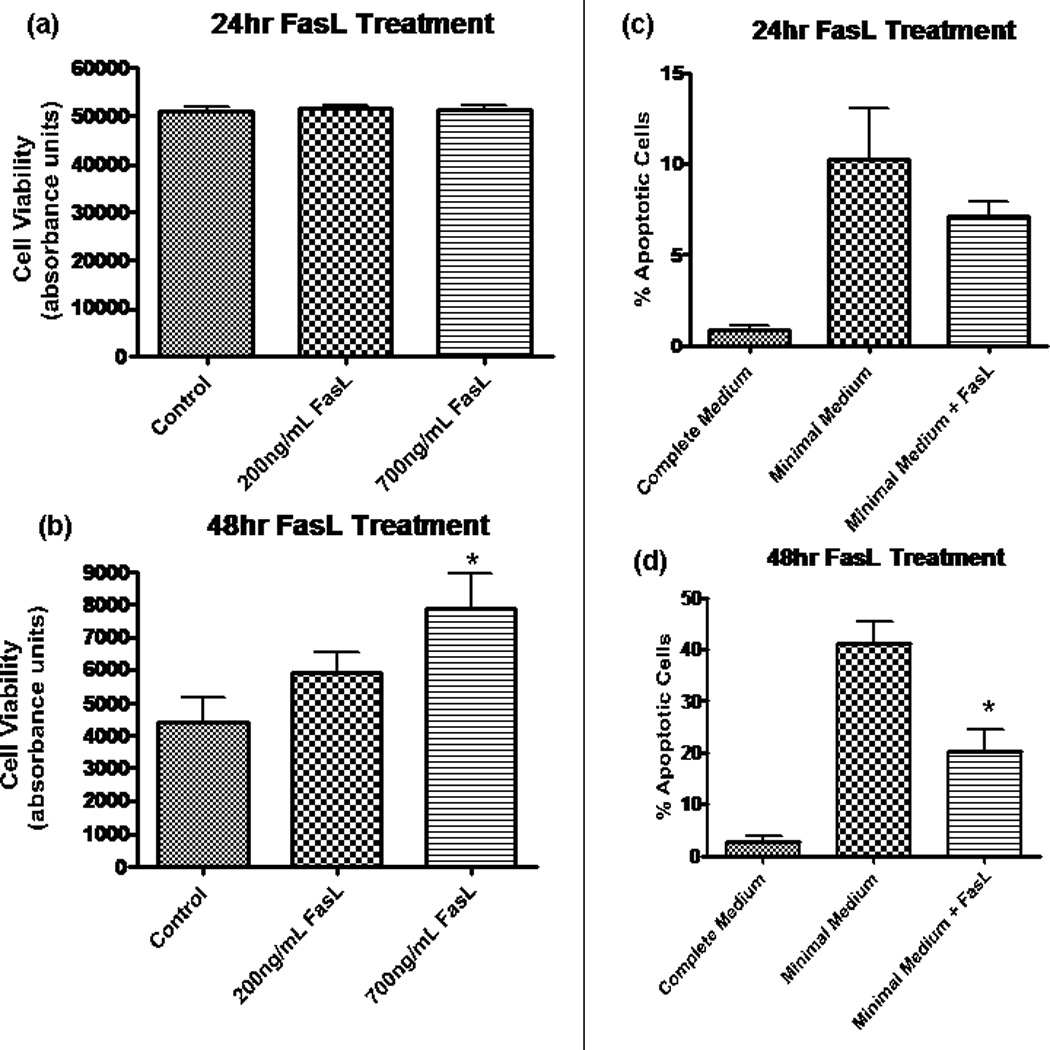
Fas activation promotes NPC survival by decreasing apoptosis. In a and b, fluorescence was measured by using Fluostar Galaxy spectrophotometry software, and the y-axis (absorbance) is in arbitrary units and is equivalent to cell viability. a: Calcien AM assay revealed no change in cell viability after 24 hr in minimal media at two different concentrations of FasL. b: At 48 hr, there was a dose-dependent increase in cell viability for treated NPCs. The difference was statistically significant at 700 ng/ml (*P < 0.05, n = 8) by ANOVA. y-Axis (absorbance) is equivalent to cell viability. c, d: Results from TUNEL assay experiments, which allow for quantification of apoptotic cells by labeling broken strands of DNA. Cells treated with FasL (200 ng/ml) in minimal medium are compared with control cells grown in minimal medium. Healthy NPCs grown in complete medium (includes EGF and FGF) provide a negative control (leftmost column). c: At 24 hr following growth factor removal, there is a trend toward a decreased percentage of apoptosis in NPCs treated with FasL. d: A significantly decreased amount of apoptosis (P < 0.01, n = 4) was observed in NPCs treated with FasL treatment for 48 hr in the absence of growth factor.
